Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into medical communication can streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve patient outcomes. Given how AI is becoming a part of healthcare and medical communication industries, it necessitates ethical implementation of AI to mitigate risks. This blog explores the ethical considerations, guidelines, and strategies for preparing an AI-enabled future in medical communication.
Speed Up the Writing Process?
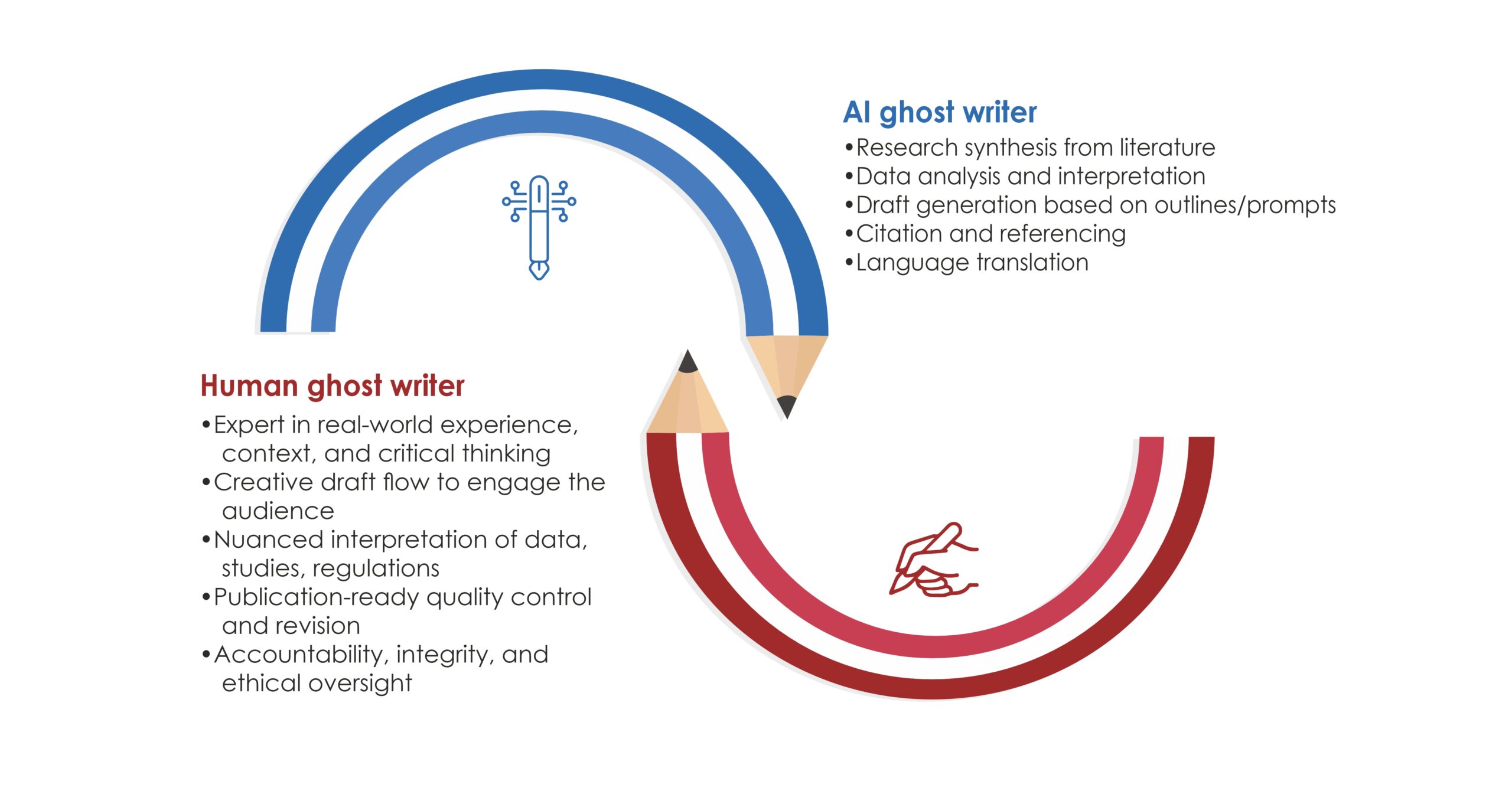
One of the most promising applications of AI in medical communication is its ability to streamline the writing process. AI-powered writing assistants can analyze vast amounts of data, synthesize information, and generate coherent and structured text that saves valuable time by automating tasks such as research, drafting, and editing.
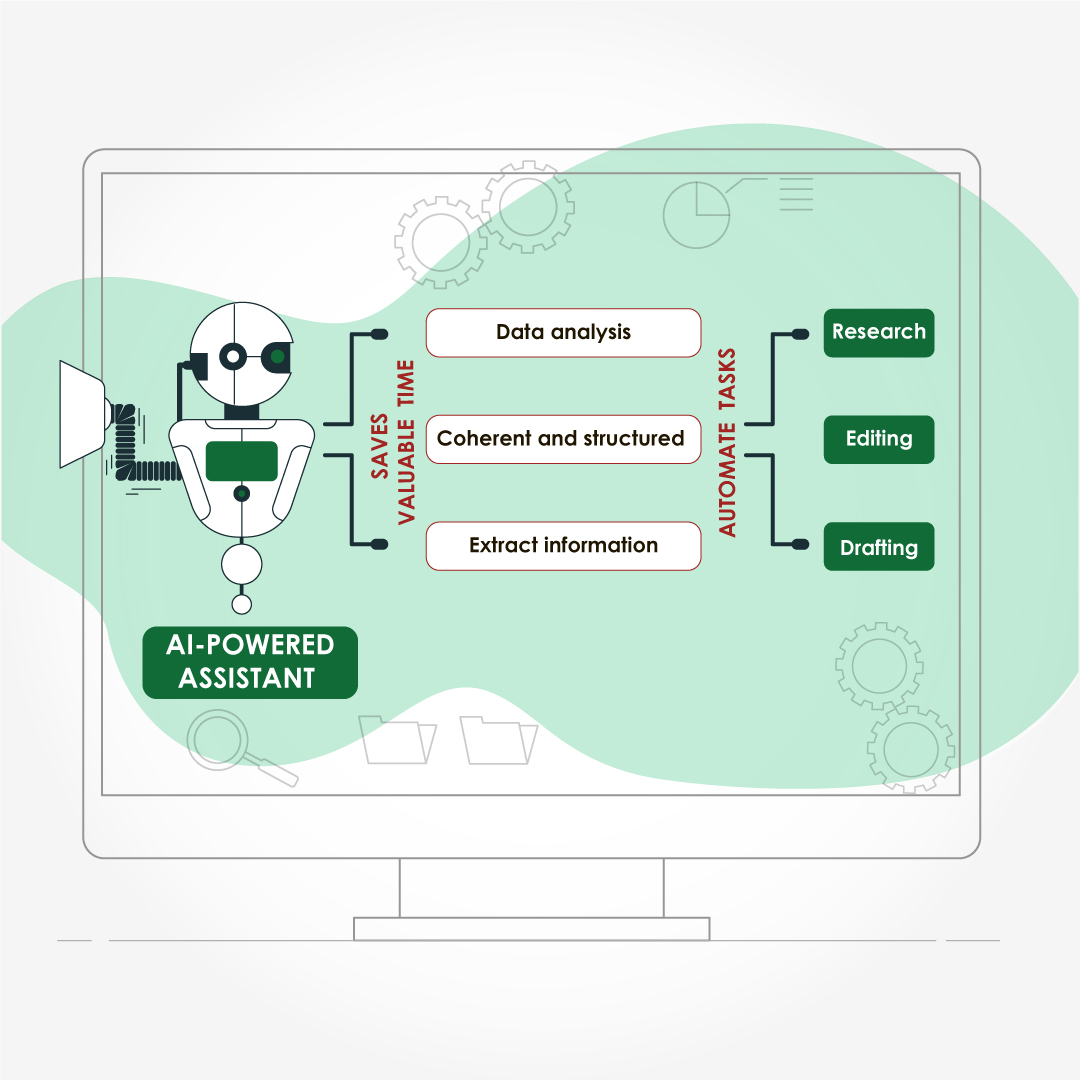
Additionally, AI can assist in generating first drafts of documents, such as research reports, patient education materials, or even scientific publications. By providing a solid foundation, AI can accelerate the writing process, enabling medical communicators to focus on refining and polishing the content, rather than starting from scratch.
Guidelines for Using Generative AI Tools
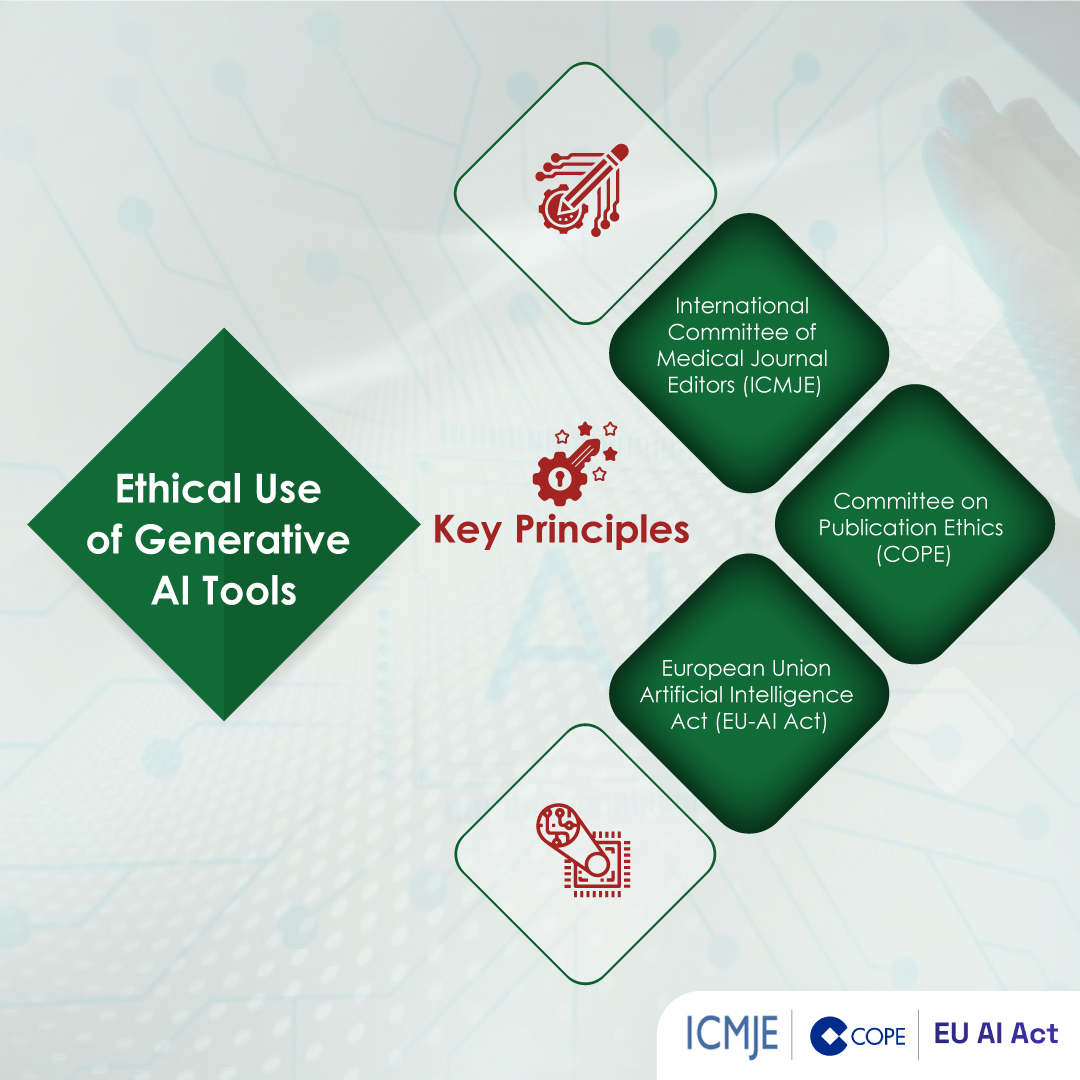
As AI-powered writing tools become more prevalent, concerns have risen regarding their potential misuse, particularly in scientific publications. To address these concerns, various organizations and publishers have established guidelines and policies governing the ethical use of AI in scientific writing.
The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) is a leading authority on publishing standards in the medical field. As per ICMJE guidelines:
- Transparency: Disclose the use of AI tools in manuscripts and clearly distinguish AI-generated content from human-written content. This transparency is crucial to maintain the integrity of scientific publications and allow readers to understand the extent to which AI was involved in the writing process.
- Accountability: Take responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the content generated by AI tools. This includes verifying the information, ensuring proper citation, and preventing the propagation of misinformation or biased content. By adhering to these guidelines, authors can leverage the efficiency of AI while maintaining the highest standards of research integrity.
On the other hand, the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE), an organization dedicated to promoting ethical practices in scholarly publishing, recommends that authors disclose the use of AI tools and take responsibility for the content generated by these tools.
Additionally, COPE emphasizes the importance of human oversight to ensure that AI-generated content is accurate, relevant, and properly cited. Authors should not present AI-generated content as their original work or misrepresent the extent of AI involvement in the writing process. COPE also advises publishers and editors to establish clear policies and guidelines for the use of AI in scholarly publications to maintain transparency and accountability.
The European Union (EU) has taken a proactive approach to regulating AI technologies with the proposed AI Act. This comprehensive legislation aims to establish a framework for the ethical development, deployment, and use of AI systems within the EU. Similarly, the EU-AI ACT recommends that authors disclose the use of AI tools and take responsibility for the content generated by these tools, and human oversight, additional key principles are:
- Robustness and Safety: AI systems must be robust, secure, and reliable, minimizing potential risks and ensuring the safety of users.
- Privacy and Data Governance: The development and use of AI systems must respect privacy rights and adhere to strict data governance practices, protecting personal data and preventing unauthorized access or misuse.
- Diversity, Non-discrimination, and Fairness: AI systems should be designed and deployed in a way that promotes diversity, avoids discrimination, and ensures fairness for all individuals and groups.
- Societal and Environmental Well-being: The development and use of AI systems should consider their potential impact on society and the environment, promoting sustainable and socially responsible practices.
Challenges in Implementing the EU AI Act
While the EU AI Act represents a significant step towards establishing ethical guidelines for AI use, its implementation faces several challenges:
- Scope and Definition: Clearly defining the scope of “high-risk” AI systems and establishing precise criteria for classification can be complex, given the rapid evolution of AI technologies.
- Compliance and Enforcement: Ensuring compliance with the AI Act across diverse industries and sectors will require robust enforcement mechanisms and international cooperation.
- Balancing Innovation and Regulation: Striking the right balance between promoting innovation and imposing necessary regulations to mitigate risks can be challenging, as overly restrictive measures may stifle technological progress.
- Technical Challenges: Implementing requirements such as transparency, robustness, and explainability can be technically complex, especially for advanced AI systems like deep learning models.
- Global Harmonization: Aligning the EU AI Act with other international regulations and standards will be crucial to avoid fragmentation and promote a consistent global approach to ethical AI use.
Preparing for an AI-Enabled Future in Medical Communication
As AI continues to advance and become more integrated into the medical communication field, professionals must adapt and develop the necessary skills to thrive in an AI-enabled future. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Embrace Lifelong Learning: The rapid pace of technological change necessitates a commitment to continuous learning and upskilling. Medical communicators should stay updated on the latest AI developments, attend relevant training programs, and actively seek opportunities to enhance their knowledge and skills.
- Develop Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills: While AI can automate certain tasks, human expertise in critical thinking, analysis, and interpretation will remain invaluable. Medical communicators should focus on honing these skills to effectively evaluate and interpret AI-generated content and ensure its accuracy and relevance.
- Cultivate Creativity and Emotional Intelligence: AI may excel at processing data and generating content, but human creativity, empathy, and emotional intelligence are essential in medical communication. Medical communicators should nurture these uniquely human qualities to create engaging and impactful content that resonates with diverse audiences.
- Foster Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Effective integration of AI in medical communication requires collaboration between professionals from various disciplines, including healthcare, technology, ethics, and communication. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, we can leverage diverse perspectives and expertise to navigate the complexities of AI implementation.
- Advocate for Ethical AI Practices: Medical communicators should actively participate in discussions and initiatives aimed at promoting ethical AI practices within their organizations and the broader industry. This includes advocating for transparency, accountability, and adherence to established guidelines and regulations.
The integration of AI in the medical communication field presents both opportunities and challenges. While AI can potentially speed up the writing process and enhance efficiency, it is crucial to navigate its use ethically and responsibly. The EU AI Act provides a comprehensive framework for ethical AI development and deployment, addressing key principles such as human oversight, transparency, fairness, and accountability.
However, implementing these guidelines will require addressing challenges related to scope, compliance, and global harmonization. As we prepare for an AI-enabled future in medical communication, it is essential to embrace lifelong learning, cultivate critical thinking and creativity, foster interdisciplinary collaboration, and advocate for ethical AI practices. By doing so, we can harness the potential of AI while mitigating risks and ensuring that medical communication remains trustworthy, accurate, and impactful in advancing healthcare outcomes.