In latest fast-paced and dynamic enterprise environment, corporations face a myriad of risks which can notably impact their operations, reputation, and backside line. From cyber threats to market volatility, information and successfully handling these dangers is crucial for lengthy-term achievement. This is wherein the exercise of enterprise hazard assessment comes into play.
What is Enterprise Risk Assessment?
Enterprise hazard evaluation is the way of figuring out, reading, and prioritizing risks that might have an effect on a company’s ability to advantage its goals. It involves comparing both inner and external factors that might pose threats or opportunities to the commercial enterprise. By systematically assessing dangers, businesses can make informed decisions and put into effect strategies to mitigate capacity terrible effects.
The Importance of Enterprise Risk Assessment Protecting Assets: Enterprises make investments large assets of their assets, such as monetary capital, highbrow assets, and human resources. Risk assessment helps pick out functionality threats to these property and growth techniques to shield them. Enhancing Resilience: By expertise ability risks, companies can build resilience and flexibility into their operations. This lets in them to reply correctly to sudden activities and maintain continuity even inside the face of adversity. Informing Decision-Making: Risk evaluation offers choice-makers with valuable insights into the capability outcomes of several movements or conditions. This permits them to make informed picks that align with the organization’s targets and danger tolerance. Maintaining Stakeholder Confidence: Stakeholders, along with buyers, customers, and regulators, anticipate corporations to proactively control risks. Conducting normal danger assessments demonstrates a determination to transparency, responsibility, and responsible governance.
Key Steps in Enterprise Risk Assessment
Establishing Objectives: Clearly outline the goals and scope of the danger assessment manner. This includes figuring out the vital aspect areas and methods within the organization so as to be evaluated.
Risk Identification: Identify ability risks by collecting data from several resources, together with historical records, industry developments, and input from stakeholders. Classify risks into lessons which includes strategic, financial, operational, and compliance.
Risk Analysis: Assess the chance and potential effect of recognized dangers. This can also additionally contain quantitative analysis, consisting of monetary modeling or state of affairs planning, as well as qualitative assessments primarily based totally on expert judgment.
Risk Evaluation: Prioritize risks primarily based totally on their significance and urgency. Consider elements which include the significance of ability losses, the chance of prevalence, and the business enterprise’s risk urge for food.
Risk Treatment: Develop and placed into effect techniques to manipulate and mitigate diagnosed dangers. This may encompass hazard avoidance, hazard cut price, chance switch, or chance attractiveness, counting on the character of the danger and the organization’s targets.
Monitoring and Review: Continuously display screen and examine the effectiveness of risk control strategies. Regularly update risk tests to mirror changes within the business surroundings, rising threats, or new possibilities.
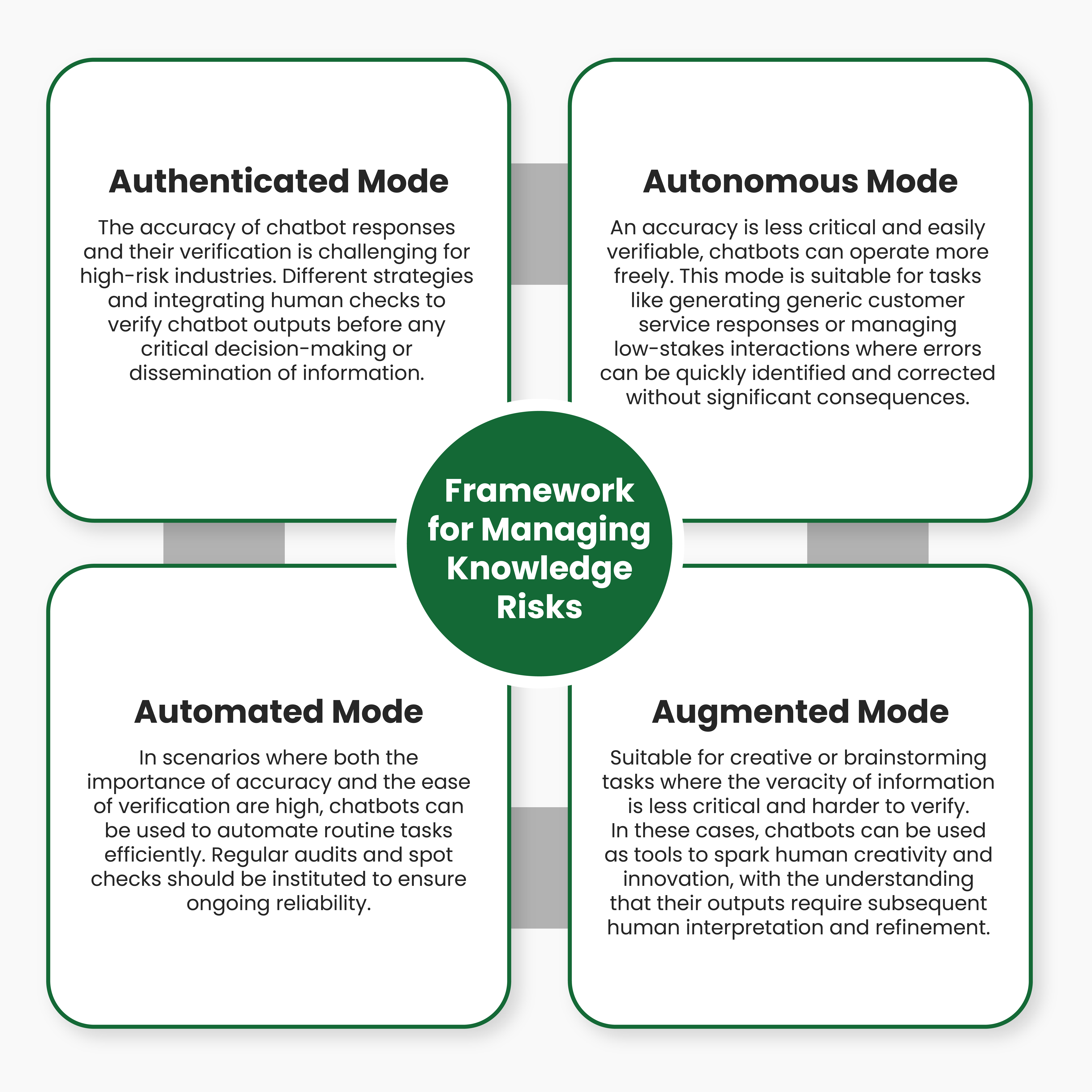
Click Here:- Beware of Botstuff: Managing the Knowledge Risks from AI Chatbots
Common Challenges in Enterprise Risk Assessment
Data Quality and Availability: Obtaining correct and reliable facts for chance evaluation may be hard, specially in complicated and rapidly changing environments.
Integration Across Functions: Risk assessment regularly calls for collaboration and coordination at some stage in one-of-a-kind departments and business enterprise devices. Ensuring alignment and consistency may be difficult, mainly in massive businesses with numerous operations.
Risk Perception Bias: Individuals may also recognize and prioritize risks in every other way based mostly on their roles, studies, and biases. It’s important to foster open communique and numerous perspectives to mitigate the impact of cognitive biases.
Emerging Risks: Identifying and assessing rising dangers, which include technological disruptions or regulatory changes, calls for proactive tracking and foresight. Organizations ought to live vigilant and adaptable to anticipate and respond to these evolving threats.
Best Practices for Effective Enterprise Risk Assessment
Top-Down Commitment: Senior leadership must display a willpower to chance control and actively assist the threat assessment system. This allows foster a lifestyle of chance awareness and duty sooner or later of the organization.
Holistic Approach: Take a holistic view of hazard with the useful resource of thinking about both inner and outdoor factors, in addition to their interdependencies. This guarantees whole insurance and minimizes blind spots within the chance assessment manner.
Continuous Improvement: Risk assessment is not a one-time workout however an ongoing method. Continuously evaluate and refine risk manage strategies based on comments, commands observed out, and changing circumstances.
Risk Communication: Effectively communicate dangers and mitigation strategies to stakeholders at all degrees of the company. Use clean and available language to facilitate statistics and purchase-in.
Utilize Technology: Leverage era system and structures to streamline and automate the threat evaluation technique. This can enhance performance, accuracy, and scalability, in particular in large or complicated agencies.
Conclusion
Enterprise hazard assessment is a crucial aspect of powerful risk manage and strategic choice-making. By systematically identifying, reading, and mitigating dangers, agencies can beautify resilience, guard property, and seize possibilities for growth. While the gadget may additionally gift disturbing situations, following quality practices, and fostering a lifestyle of danger focus can help businesses navigate uncertainty and thrive in an ever-converting enterprise landscape.









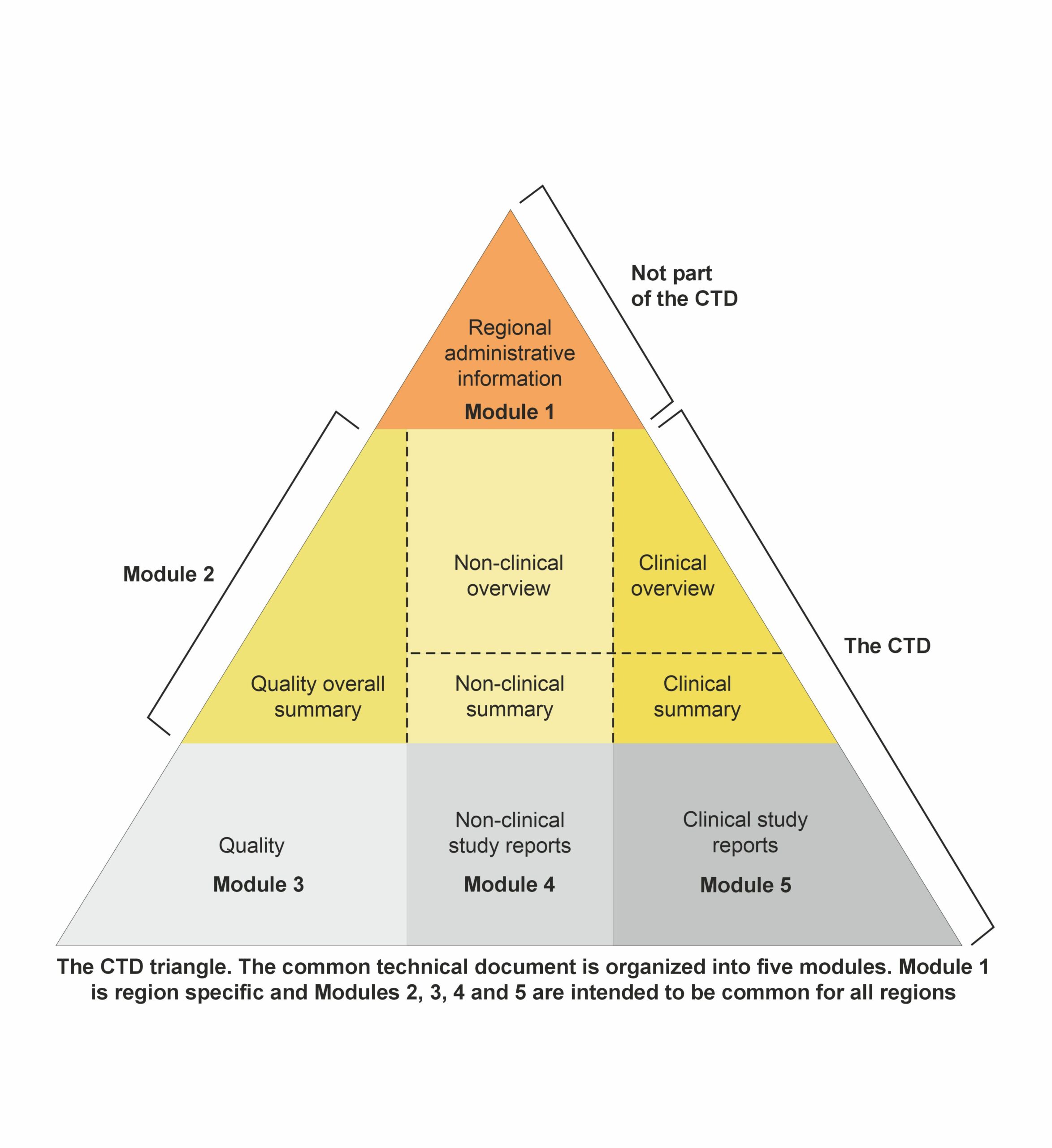 Module 1: Administrative and prescribing information
Module 1: Administrative and prescribing information

 Challenges and Considerations in CSR Preparation
Challenges and Considerations in CSR Preparation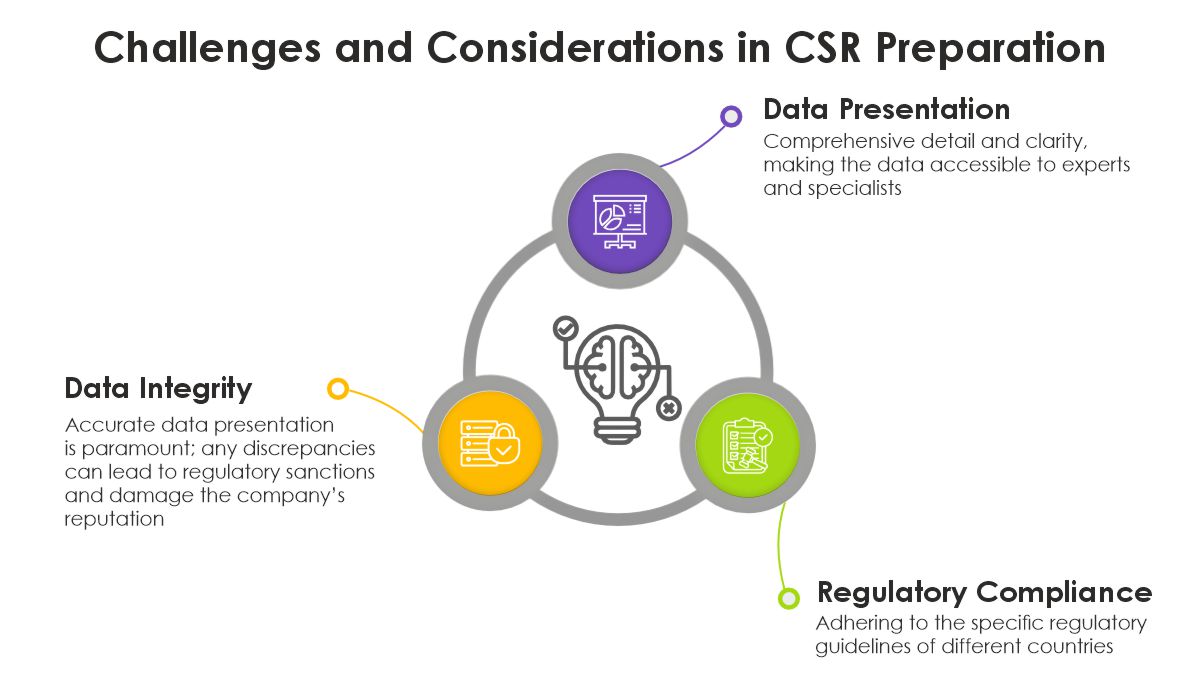 The Future of CSR
The Future of CSR

