Journal metrics play a crucial role in evaluating the significance and influence of scholarly journals in academic publishing. These metrics serve as quantitative tools that help researchers, institutions, and funding bodies assess the impact of journals and, by extension, the research published within them. Although the impact factor is perhaps the most well-known of these metrics, it is by no means the only one. This blog will dive into various journal metrics, including the impact factor, h-index, and altmetrics, and discuss their significance, limitations, and broader implications for the academic community.
The Impact Factor: A Traditional Measure
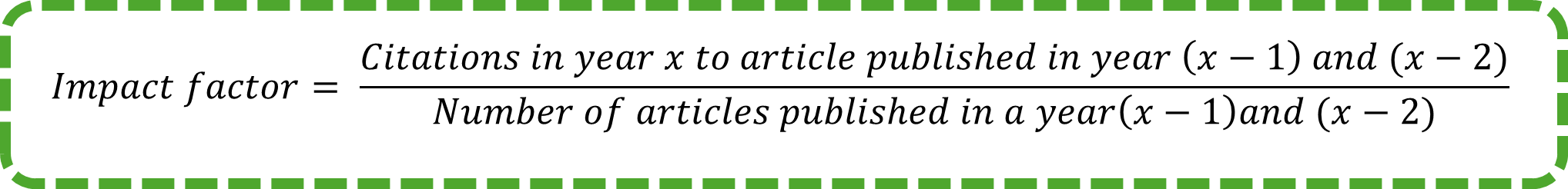
The quest to quantify scholarly impact began in the mid-20th century as the volume of scientific literature exploded. Eugene Garfield’s introduction of the Science Citation Index in 1964 and the subsequent development of the impact factor in 1975 marked significant milestones in bibliometrics. The formula for calculating the impact factor is as follows:
Significance of the Impact Factor
- Indicator of Influence: The impact factor is widely regarded as an indicator of a journal’s influence and prestige within its field. Higher impact factor values are often associated with prestigious journals.
- Decision-Making Tool: Researchers use the impact factor to decide where to submit their work, and institutions use it to assess research output and make funding decisions
Limitations of the Impact Factor
- Disciplinary Variations: Different academic fields have different citation behavior. For instance, journals in the natural sciences often have higher impact factors than those in the humanities and social sciences do.
- Short-Term Focus: The two-year citation window may not adequately reflect the long-term impact of research, especially in fields where citations accumulate slowly over time.
- Susceptibility to Manipulation: Journals may adopt strategies to artificially inflate their impact factors, such as encouraging self-citations or publishing review articles that tend to receive more citations.
- Narrow Scope: The impact factor focuses solely on citation counts, ignoring other aspects of scholarly influence, such as societal impact, educational value, or policy influence.
The h-Index: A Measure of Individual and Journal Impact
Introduced by physicist Jorge Hirsch in 2005, aims to measure both the productivity and citation impact of an individual researcher or a journal. An entity has an h-index of h if h of its N papers have at least h citations each, and the other N – h papers have fewer than h citations each.
Significance of the h-Index
- Balanced Metric: The h-index balances quantity (number of publications) and quality (number of citations), providing a more comprehensive measure of impact.
- Comparative Tool: This is useful for comparing researchers or journals within the same field, helping to identify influential contributors.
Limitations of the h-Index
- Field-Specific Bias: Like the impact factor, the h-index can be biased by field-specific citation practices, which makes cross-disciplinary comparisons problematic.
- Age Sensitivity: The h-index tends to favor senior researchers who have had more time to accumulate citations, potentially disadvantaging early-career researchers.
- Ignores Context: It does not account for the context of citations, such as whether citations are positive or negative, nor does it consider collaborative efforts where authorship contributions may vary.
Altmetrics: Beyond Traditional Citations
This represents a diverse set of measures that capture the attention research outputs receive online. This includes social media mentions, news coverage, blog posts, and other online platforms. Tools like Altmetric.com and PlumX provide aggregated altmetric scores for individual research output.
Significance of Altmetrics
- Broader Impact: Altmetrics capture the broader impact of research, including its influence on public discourse, policy, and practice, which traditional metrics may overlook.
- Timeliness: They provide real-time insights into how research is discussed and shared, offering a timely complement to traditional citation metrics.
- Engagement: Altmetrics highlights engagement with a wider audience beyond the academic community, reflecting the societal relevance and reach of research.
Limitations of Altmetrics
- Data Quality: The reliability and consistency of altmetric data can vary, as it depends on tracking diverse and sometimes ephemeral online activities.
- Potential for Gaming: Social media activities can be easily manipulated, raising concerns regarding the authenticity of altmetric scores.
- Field-Specific Bias: Certain fields may naturally attract more online attention than others, skewing altmetric comparisons across disciplines.
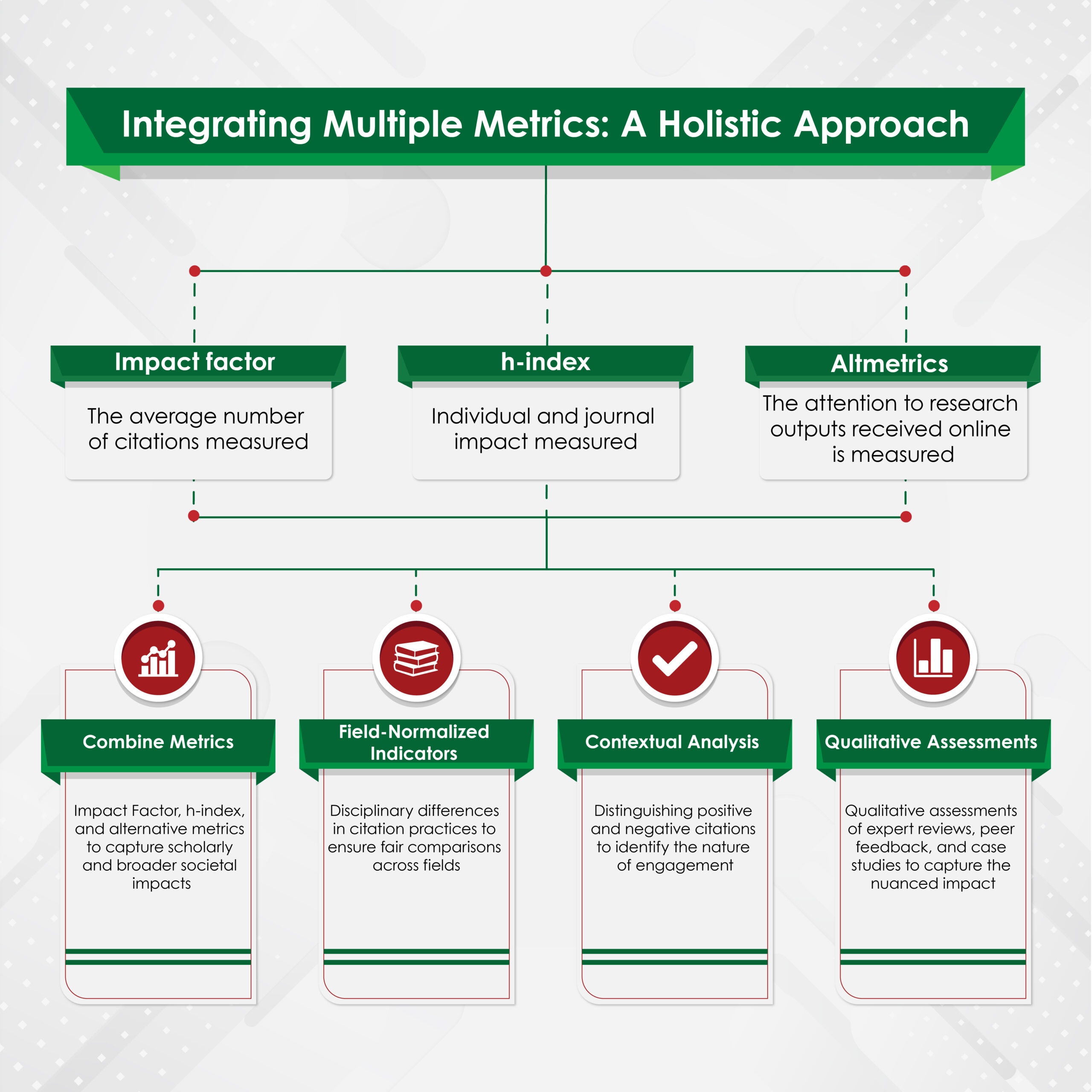
Integrating Multiple Metrics: A Holistic Approach
While each of these metrics offers valuable insights, none is without flaws. A holistic approach that integrates multiple metrics can provide a more comprehensive evaluation of journal impact. Some strategies for achieving this are as follows:
- Combine Metrics: Use a combination of traditional metrics (impact factor, h-index) and alternative metrics (altmetrics) to capture both scholarly and broader societal impacts.
- Field-Normalized Indicators: Employ field-normalized indicators to account for disciplinary differences in citation practices, and ensure fair comparisons across fields.
- Contextual Analysis: Consider the context of citations and altmetric mentions, distinguishing between positive and negative citations, and identifying the nature of online engagement.
- Qualitative Assessments: Complement quantitative metrics with qualitative assessments, such as expert reviews, peer feedback, and case studies, to capture the nuanced impact of research.
The Way Forward
The landscape of journal metrics is evolving, with new tools and methodologies continually being developed to address the limitations of existing metrics. Some emerging trends are as follows:
- Open Metrics: The movement towards open science is driving the development of open metrics, which are transparent, reproducible, and freely accessible. These metrics aim to provide a more democratic and inclusive assessment of research impact.
- Responsible Metrics: There is a growing emphasis on responsible metrics that advocate the ethical and responsible use of metrics in research assessment. Initiatives like Declaration on Research Assessment (DORA) and the Leiden Manifesto provide guidelines for the responsible use of metrics.
- AI and Big Data: Advances in artificial intelligence and big data analytics are enabling the development of sophisticated metrics that can analyze vast amounts of data and provide deeper insights into research impact.
Understanding journal metrics is essential for navigating the complex landscape of academic publishing. While traditional metrics like the impact factor and h-index offer valuable insights into scholarly influence, they have significant limitations. Altmetrics provides a complementary perspective by capturing the broader societal impact of research. However, no single metric can fully capture the multifaceted nature of research impact.
A holistic approach that integrates multiple metrics and considers both quantitative and qualitative assessments is crucial for the comprehensive evaluation of journal impact. As the landscape of journal metrics continues to evolve, researchers, institutions, and funding bodies need to stay informed about emerging trends and adopt responsible practices in research assessment.
At Turacoz, we integrate multiple metrics for journal assessment, combining traditional measures like the IF and h-index with innovative altmetrics. This comprehensive approach captures both scholarly influence and broader societal engagement, providing nuanced insights. Our expertise in academic publishing metrics helps clients make informed decisions about where to publish and how to evaluate research impact. Visit www.turacoz.com or contact [email protected] to discover how we can enhance your research strategy and maximize your work’s visibility and influence.