Recently, while working on a project about preeclampsia during pregnancy, our team was startled to learn that preeclampsia is one of the most common hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, accounting for 2%–8% of pregnancy-related complications, more than 50,000 maternal deaths, and over 500,000 fetal deaths worldwide.1 Yet, many women are unaware that early diagnosis and prompt symptomatic management can help prevent such maternal and neonatal complications. The need of the hour is to empower women with knowledge and awareness about their health so that they can proactively prioritize their well-being while juggling multiple responsibilities.
Below are ten essential steps all women should undertake to keep all diseases at bay for themselves and their families.
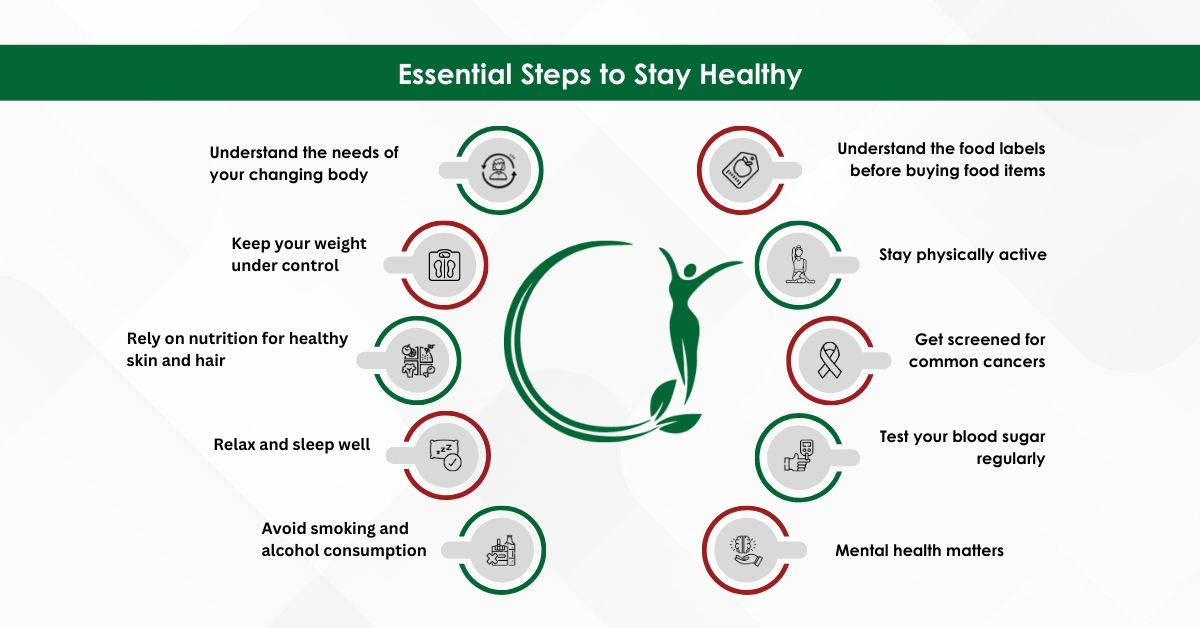
Understand the food labels before buying food items
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the increased consumption of processed foods high in salt, sugar, and fat is a key driver of a global obesity crisis. Currently, more than a billion people live with obesity,2 and an estimated 17 million early deaths occur every year due to noncommunicable diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.3 Studies have shown that some of the most frequently present additives in children’s food include bisphenols, phthalates, perfluoroalkyl chemicals, perchlorates, pesticides, nitrates and nitrites, artificial food colors, monosodium glutamate, and aspartame—all of which can be harmful to a child’s growth and development. As women are more involved in feeding their families, they must understand the nutritional labels and their implications. The next time you pick up a packet of your favorite snack, do not blindly trust the brand—read the fine print carefully.
Stay physically active
A recent study involving 5000 postmenopausal women in California supports the importance of regular physical activity and reduced sedentary time in lowering mortality risk, regardless of their genetic predisposition for longevity. Women who do strength training exercises 2–3 times a week are more likely to live longer and have a 30% lower risk of death from heart disease compared to those who do not exercise.4
Get screened for common cancers
According to the American Cancer Society, breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women, with the lifetime risk of 1 in 43.5 Young women are more likely to develop aggressive forms of breast cancer, often linked to genetic factors such as inherited mutations in the BRCA genes, highlighting the importance of undergoing BRCA testing. Studies have demonstrated that early detection of breast cancer can lead to a 100% survival rate, especially when the cancer is localized.6 Another major cancer affecting women is cervical cancer, which the WHO ranks as the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women, causing 350,000 deaths in 2022.7 Persistent HPV infections are the primary cause of cervical cancer, and vaccination between the ages of 9 and 14 is an effective preventive measure. Studies indicate that unvaccinated women are ten times more likely to develop cervical cancer than those who are vaccinated.8 Therefore, to maintain good health and a high quality of life, women should prioritize regular checkups, early detection screenings, and staying up to date with vaccinations.
Test your blood sugar regularly
Recent studies have demonstrated that 10.5% of the adult population has diabetes,9 with nearly half unaware of their condition, leading to untreated diabetes and increasing the risk of cardiovascular (CV), renal, and neurological complications.10 Research has shown that early detection and treatment of type 2 diabetes can reduce the risk of CV complications by 29%–38%, emphasizing the importance of early detection. Regular blood sugar testing plays a vital role in this process.11 With glucometers now widely available, women can easily monitor their own and their family’s blood sugar levels, even with their busy schedules, and promptly seek medical attention if any irregularities are detected.
Mental health matters
Women are three times more likely to experience mental health issues than men.12 Poor mental health not only impacts physical well-being but also decreases workplace productivity by nearly 13%,13 with twelve billion working days lost annually due to depression and anxiety.14 Furthermore, about 10% of pregnant women and 13% of postpartum women experience mental health disorders, primarily depression, which can negatively affect both the mother’s well-being and the child’s growth and development.15 These statistics are concerning and highlight the importance of prioritizing mental health. Women can support their well-being by adopting healthy habits such as regular exercise, balanced diet, self-care, and maintaining social connections.
Understand the needs of your changing body
Menopause, marking the end of reproductive years, often lacks the attention it deserves despite its significant impact. It leads to a decline in estrogen, causing symptoms like irregular periods, hot flashes, night sweats, insomnia, vaginal dryness, and mental health challenges like mood swings, anxiety, and depression. Menopause is also a major risk factor for osteoporosis, affecting 1 in 3 women.16 Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is most effective when started within 10 years of menopause or before age 60. HRT helps relieve menopausal symptoms, prevents bone loss, and reduces the risk of fractures by 20%–40%.17 Hence, women should consult their doctor early for best results. Additionally, calcium and vitamin D supplements, a healthy diet, an active lifestyle, and cognitive behavioral therapy can help manage symptoms further.
Keep your weight under control
PCOS, hypothyroidism, Cushing’s syndrome, insulin resistance, stress, and emotional eating are the common health issues that can lead to weight gain in women. Studies show that 38%–88% of women with PCOS are either overweight or obese, which can negatively impact their menstrual and reproductive health.18 However, even a modest weight loss of 5% in obese women with PCOS can help alleviate symptoms.19 Regarding hypothyroidism, women are 8–9 times more likely to develop the condition, with the highest incidence between the ages of 30 and 50.20 Gaining a few pant sizes can be a key symptom of hypothyroidism. Women experiencing this should seek prompt medical advice and undergo appropriate treatment, as weight gain can lead to additional complications such as cardiovascular disease (CVD), joint issues, sleep apnea, and psychological distress.
Rely on nutrition for healthy skin and hair
The quest for healthy skin and hair often leads women to explore a wide range of cosmetic products. However, emerging research suggests that nutrition plays a far more significant role in maintaining and enhancing skin and hair health. Rather than relying on topical treatments, proper nutrition addresses the root causes of skin and hair concerns by supplying the body with essential nutrients. Many common chemicals found in skincare products, such as sodium lauryl sulfate, phthalates, fragrances, mineral oils, lead, and formaldehyde, can have harmful effects on the skin and other organs. In contrast, studies have shown that consuming antioxidant-rich foods can reduce photoaging by 10% over 15 years compared to diets low in antioxidants.21 Similarly, for hair health, research reveals that incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into the diet can improve scalp hydration and increase hair shine. These findings highlight how nutrition offers a safer and more effective approach to achieving and maintaining healthy skin and hair, as opposed to relying on potentially harmful cosmetics.
Relax and sleep well
Research shows that inadequate sleep negatively affects women’s mental, physical, and reproductive health, along with daily functioning. Studies reveal concerning patterns that underscore the importance of adequate sleep. Chronic sleep deprivation (less than 6 hours per night) is correlated with a higher body mass index, 22 15% increased risk of CVD, 23% higher risk of coronary heart disease,23 and increased likelihood of developing diabetes.24 .26 By adhering to a consistent good sleep routine, women may mitigate these health risks.
Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption
According to WHO data, tobacco use causes more than eight million deaths each year, whereas alcohol consumption is responsible for 2.6 million deaths.27,28 Research has shown that alcohol misuse and smoking are rising among women, posing serious health risks not only for them but also for their babies. Studies indicate that babies born to mothers who smoke are twice as likely to have a lower birth weight compared to those born to nonsmoking mothers.29 In fact, 14% of all deaths due to low birth weight are linked to tobacco use during pregnancy.29 Moreover, heavy alcohol consumption in women is associated with a more rapid onset of health conditions such as CVD, obesity, and various cancers. These findings highlight the importance of cutting back or abstaining from these habits. To stay on track, it is essential to recognize triggers, avoid situations that tempt you, find healthier coping mechanisms such as exercising or picking up new hobbies, and seek support from friends and family.
In conclusion, discipline is the key to a healthy life. By incorporating a few simple healthy habits into your daily routine, you set yourself up for a future filled with health and happiness. Take charge of your life—stay vigilant, act quickly when needed, do not hesitate to ask for help, and stay strong. Everything will fall into place. Remember, prioritizing your health and scheduling regular checkups is not just about taking care of your body, it is about empowering yourself. Staying up to date with the latest health information and educating yourself on wellness is just as important, as it helps you make informed choices and stay ahead. By prioritizing your well-being, you truly embody the strength of an empowered woman.
- Karrar SA, Martingano DJ, Hong PL. [Updated 2024 Feb 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570611/.
- One in eight people are now living with obesity. Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/01-03-2024-one-in-eight-people-are-now-living-with-obesity. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Cardiovascular disease. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)#:~:text=In%202013%2C%20WHO%20Member%20States,on%20preventing%20and%20controlling%20CVDs . Last accessed: March 2025.
- Study: Women who do strength training live significantly longer. Available at: https://globalwellnessinstitute.org/global-wellness-institute-blog/2024/05/28/study-women-who-do-strength-training-live-significantly-longer/#:~:text=Study:%20Women%20Who%20D,Access%20this%20study%20on%20exercise. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Key statistics for breast cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-cancer.html#:~:text=Breast%20cancer%20is%20the%20second,decline%20of%2044%25%20through%202022. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Li J, Guan X, Fan Z, et al. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(10):2767.
- Cervical cancer. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer#:~:text=Cervical%20cancer%20is%20the%20fourth,compared%20to%20women%20without%20HIV. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Naslazi E, Hontelez JAC, Naber SK, et al. The Differential Risk of Cervical Cancer in HPV-Vaccinated and -Unvaccinated Women: A Mathematical Modeling Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021;30(5):912-919.
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045 [published correction appears in Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2023;204:110945.
- Hossain MJ, Al-Mamun M, Islam MR. Diabetes mellitus, the fastest growing global public health concern: Early detection should be focused. Health Sci Rep. 2024;7(3):e2004.
- Herman WH, Ye W, Griffin SJ, et al. Early Detection and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Reduce Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality: A Simulation of the Results of the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment in People With Screen-Detected Diabetes in Primary Care (ADDITION-Europe). Diabetes Care. 2015;38(8):1449-1455.
- Men and women: Statistics. Available at: https://www.mentalhealth.org.uk/explore-mental-health/statistics/men-women-statistics#:~:text=Women%20between%20the%20ages%20of,the%20same%20age%20(9%25).&text=Women%20are%20twice%20as%20likely%20to%20be%20diagnosed%20with%20anxiety%20as%20men. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Happy workers are 13% more productive. Available at: https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2019-10-24-happy-workers-are-13-more-productive. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Mental health at work. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-at-work. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Perinatal mental health. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/mental-health-and-substance-use/promotion-prevention/maternal-mental-health. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Available at: https://thebms.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/06-BMS-ConsensusStatement-Prevention-and-treatment-of-osteoporosis-in-women-SEPT2023-A.pdf. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Gosset A, Pouillès JM, Trémollieres F. Menopausal hormone therapy for the management of osteoporosis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;35(6):101551.
- Barber TM. Why are women with polycystic ovary syndrome obese? Br Med Bull. 2022;143(1):4-15.
- Treatment, polycystic ovary syndrome. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/polycystic-ovary-syndrome-pcos/treatment/#:~:text=In%20overweight%20women%2C%20the%20symptoms,a%20significant%20improvement%20in%20PCOS. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Chiovato L, Magri F, Carlé A. Hypothyroidism in Context: Where We’ve Been and Where We’re Going. Adv Ther. 2019;36(2):47-58.
- Hughes MCB, Williams GM, Pageon H, et al. Dietary Antioxidant Capacity and Skin Photoaging: A 15-Year Longitudinal Study. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141(4S):1111-1118.e2.
- Papatriantafyllou E, Efthymiou D, Zoumbaneas E, et al. Sleep Deprivation: Effects on Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance. Nutrients. 2022;14(8):1549.
- Hoevenaar-Blom MP, Spijkerman AM, Kromhout D, et al. Sleep duration and sleep quality in relation to 12-year cardiovascular disease incidence: The MORGEN study. Sleep. 2011;34(11):1487-1492.
- Darraj A. The Link Between Sleeping and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2023;15(11):e48228.
- The close relationship between sleep and mental health. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/sleep-and-mental-health. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Beroukhim G, Esencan E, Seifer DB. Impact of sleep patterns upon female neuroendocrinology and reproductive outcomes: A comprehensive review. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022;20(1):16.
- Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol#:~:text=Worldwide%2C%202.6%20million%20deaths%20were,per%20100%20000%20people%2C%20respectively. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tobacco#:~:text=Tobacco%20kills%20up%20to%20half,are%20Parties%20to%20this%20treaty. Last accessed: March 2025.
- Tobacco in Australia, facts and issues. Available at: https://www.tobaccoinaustralia.org.au/chapter-3-health-effects/3-8-child-health-and-maternal-smoking. Last accessed: March 2025.