Medical writing is a specialized discipline within the clinical research domain, focused on preparing scientific documents. These documents must adhere strictly to guidelines regarding their structure, content, and format. Narrative writing is a crucial component of medical writing services, particularly in crafting patient narratives to summarize identified adverse events (AEs) and establish causal relationships with investigational drugs. These narratives, typically one to four pages long, are submitted alongside the clinical study report (CSR), with large trials potentially generating hundreds of narratives. Sponsors often outsource narrative writing activities to effectively manage the demands of cost, time, and quality in project management. We at Turacoz Healthcare Solutions have been in this business for a decade catering to diverse clientele.
This blog aims to guide medical writers in understanding the narrative writing process (NWP), regulatory standards, challenges, mitigation strategies, and emerging trends in narrative automation. Patient narratives summarize AEs observed in clinical trial patients, including criteria such as death, serious AEs (SAEs), events of special interest, AEs leading to drug discontinuation, and adjudication events. Structured with clarity and precision, they provide medical and scientific context, typically following a logical flow:
- Description of the event’s clinical course, including timing concerning drug administration.
- Details on the nature, intensity, and outcome of the event.
- Relevant laboratory findings and administered treatments.
- Actions taken regarding the study drug.
- Postmortem findings (if applicable) and assessments of causality by the investigator and sponsor if necessary.
Moreover, patient identifiers, demographics, medical history, and concurrent medications should also be included to provide comprehensive context.
Types of Narratives
- Descriptive Narratives: Focused on providing a detailed account of the research process, from study design and methodology to data collection and analysis. Descriptive narratives aim to paint a comprehensive picture of the research endeavor, guiding readers through each phase with clarity and precision.
- Analytical Narratives: These delve deeper into the interpretation and implications of research findings. They analyze the data within the context of existing literature, identify patterns or trends, and offer insights that contribute to advancing scientific knowledge or update clinical practice.
- Persuasive Narratives: They aim to convince readers of the significance and validity of the research findings. Leveraging compelling storytelling techniques, persuasive arguments, and evidence-based reasoning to sway the reader’s opinion or influence decision-making processes.
Process of Narrative writing
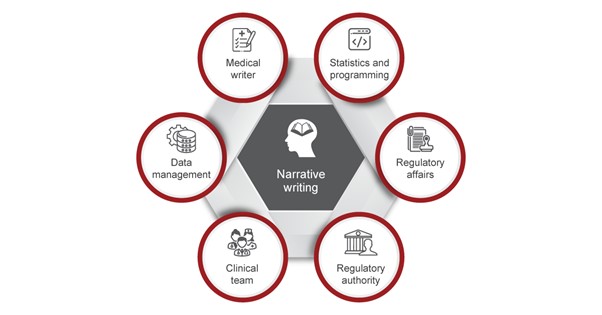
Narrative writing is a complex process involving various departments that begins with template finalization which is a crucial step in the NWP as it avoids subjectivity.
- Research and Planning: Begin by conducting thorough research on the topic, familiarizing yourself with existing literature, and identifying key research questions and objectives. Plan the narrative structure, outlining the main sections and their respective content.
- Drafting: Write the initial draft of the narrative, focusing on clarity, coherence, and engagement. Pay attention to storytelling elements such as narrative arc, character development (e.g., study participants), and thematic coherence.
- Revision and Editing: Review the draft critically, refining the narrative for clarity, accuracy, and conciseness. Eliminate unnecessary details, strengthen the argumentation, and ensure consistency in style and tone. Seek feedback from peers or subject matter experts to enhance the quality of the narrative.
- Finalization: Incorporate feedback and make final revisions to the narrative. Ensure adherence to formatting guidelines and standards for scientific writing. Proofread the document meticulously to correct any errors in grammar, punctuation, or spelling.

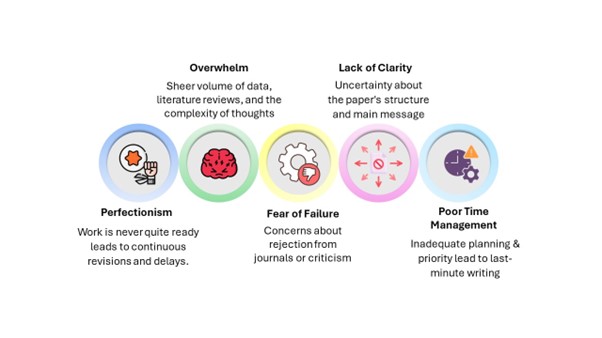
Challenges in NWP
Balancing Objectivity and Subjectivity: Striking the right balance between objective reporting of facts and subjective interpretation of findings can be challenging. Avoiding bias while presenting research results objectively requires careful attention to language and tone.
Complexity of Scientific Concepts: Communicating complex scientific concepts in a clear and accessible manner poses a significant challenge. Medical writers must employ effective strategies such as analogy, visualization, and plain language to enhance understanding among diverse audiences.
Time Constraints: Meeting tight deadlines while ensuring quality and accuracy can be daunting. Effective time management, prioritization, and collaboration with team members are essential to overcoming this challenge.
Effective Ways to Execute Narrative Writing Process
- Collaborative Approach: Foster collaboration and communication among multidisciplinary team members, including researchers, clinicians, statisticians, and editors. Leverage each team member’s expertise to enrich the narrative and ensure its accuracy and relevance.
- Iterative Writing Process: Embrace an iterative writing process that involves multiple rounds of drafting, revision, and feedback. This iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and refinement of the narrative until it achieves optimal clarity and impact.
- Utilization of Technology: Harness the power of technology tools and resources to streamline the narrative writing process. Digital platforms, reference management software, and writing assistance tools can enhance productivity, organization, and collaboration among team members.
Automation of Narratives
The automation of narrative writing offers promising opportunities to streamline and optimize the process. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms, machine learning techniques, and artificial intelligence (AI) platforms can analyze data, generate insights, and draft narrative content with increasing accuracy and efficiency. While automation cannot replace human creativity and critical thinking, it can complement the work of medical writers by automating repetitive tasks and providing valuable support in data analysis and interpretation.
Tips for Narrative Writing
- Know Your Audience: Tailor the narrative to the needs and preferences of the target audience, who could be healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, or patients.
- Focus on Clarity and Simplicity: Use clear, concise language and avoid unnecessary jargon or technical terms. Ensure that the narrative is accessible and understandable to readers with varying levels of expertise.
- Engage the Reader: Capture the reader’s attention from the outset with a compelling introduction and maintain engagement throughout the narrative with vivid storytelling and relevant examples.
- Stay True to the Science: Uphold scientific integrity and accuracy in all aspects of the narrative, from data interpretation to citation of sources. Avoid sensationalism or exaggeration of findings.
- Seek Feedback: Welcome constructive feedback from peers, mentors, or subject matter experts to improve the quality and effectiveness of the narrative.
Narrative writing in clinical research is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a combination of creativity, analytical rigor, and effective communication skills. By adhering to the guidelines outlined in this guide and embracing innovative approaches and technologies, medical writers can master the art of narrative writing and contribute to advancing scientific knowledge and improving patient care outcomes.