In medical and scientific writing, effectively communicating complex information is vital to ensuring that research findings, clinical data, and patient outcomes are clearly understood. As data becomes more abundant, healthcare professionals and researchers are increasingly relying on data visualization as a key tool for simplifying complex datasets. For medical writers, data visualization can transform written content into visually engaging and informative material that enhances comprehension and decision-making.
The Importance of Data Visualization
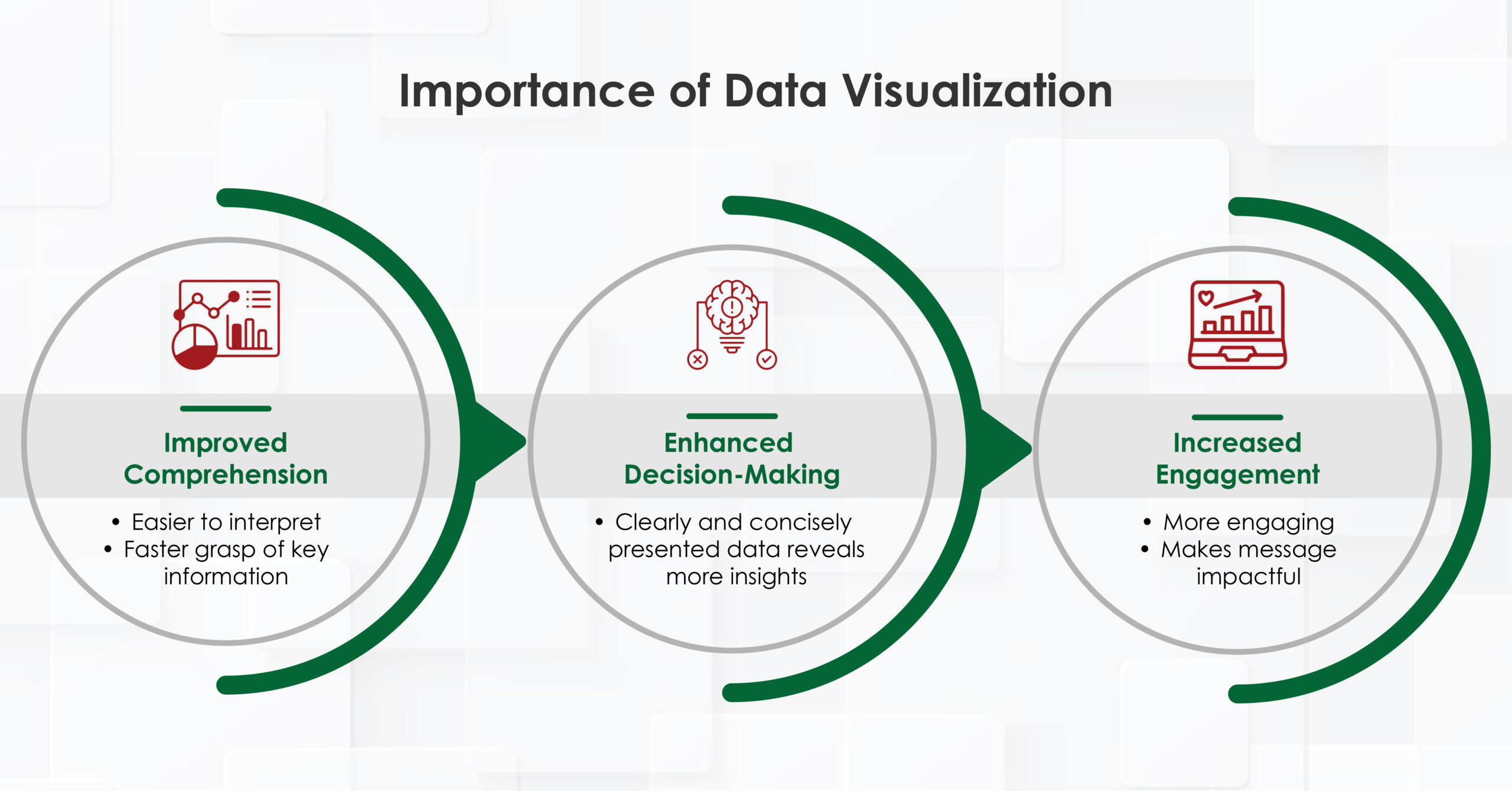
- Improved comprehension: Complex data is easier to interpret when presented visually, helping readers grasp key information faster.
- Enhanced decision-making: Healthcare professionals can make more informed decisions when data is presented in a clear, concise manner.
- Increased engagement: Visual content is more engaging and memorable, making the message more impactful.
How Data Visualization is Used in Healthcare
In healthcare, data visualization is used in various ways, from monitoring patient health to evaluating healthcare system performance. Medical writers often contribute to these processes by creating documents and reports that incorporate visual elements, helping different stakeholders—healthcare providers, researchers, and patients—make sense of the data.
- Patient Monitoring: In clinical settings, healthcare professionals use dashboards and visual reports to track patient health metrics in real-time. This allows for quick identification of abnormal trends, such as sudden spikes in heart rate or blood pressure, prompting timely interventions.
- Clinical Research: Data visualization is essential for presenting research findings, making it easier to communicate complex statistical data from clinical trials or population studies. Medical writers can use charts, graphs, and other visual elements to summarize results, allowing readers to quickly grasp significant findings and their implications.
- Public Health Initiatives: Public health authorities often rely on visual tools, such as heat maps and bar graphs, to track disease outbreaks, vaccination rates, or healthcare access. Visualizations help these agencies monitor trends, allocate resources efficiently, and educate the public.
- Decision Support Systems: Decision support tools that use visual analytics assist clinicians in selecting appropriate treatments, assessing risks, and predicting patient outcomes. Visual dashboards and algorithms can help professionals make quicker, evidence-based decisions.
For medical writers, understanding the role of visualization in healthcare allows them to craft content that aligns with the needs of healthcare providers and researchers while making complex data more accessible.
Infographics for Visualizing Medical Data
Infographics have become a powerful tool for medical writers to communicate data in a more engaging format. By combining visual elements like charts, icons, and text, infographics present data in a way that is easy to understand. This is particularly important in medical writing, where the audience can range from highly specialized clinicians to patients with limited medical knowledge.
For medical writers, infographics serve multiple purposes:
- Patient Education: Infographics can break down medical information into clear, easy-to-follow steps, making it easier for patients to understand their condition, treatment options, or preventative measures.
- Scientific Communication: In research articles or reports, medical writers can use infographics to highlight key findings, summarizing the most important data points in a visually appealing way.
- Public Health Campaigns: Infographics are often used in public health messaging to inform the general population about important health issues, such as vaccination schedules, hygiene practices, or disease prevention.
Incorporating infographics into medical writing not only enhances clarity but also increases the likelihood that the content will be shared and referenced, broadening its reach and impact.
Posters in Hallways and Doctors’ Offices: A Thing of the Past?
For many years, posters in hospitals, doctors’ offices, and clinic hallways served as a primary way to communicate health information. However, in today’s digital age, static posters are being replaced by more dynamic and interactive forms of data visualization. Medical writers now can move beyond traditional posters and embrace digital communication tools, such as:
- Interactive Screens: Digital displays in waiting rooms and hallways can present rotating information, such as patient education videos, real-time health statistics, or news updates. This digital shift offers more flexibility in updating content and engaging patients.
- Online Platforms: With the rise of telemedicine and digital health apps, patients are accessing health information online. Medical writers can create interactive infographics, videos, and other digital content tailored to these platforms.
While posters may still have a role in certain settings, digital tools allow medical writers to create more dynamic, customizable content that can be easily updated and widely distributed.
Graphical Reports on Clinical Data and Performance
Medical writers play a crucial role in creating these reports, which often include:
- Visual Performance Dashboards: Dashboards can track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as patient satisfaction, readmission rates, and average hospital stays. These visualizations allow healthcare administrators to monitor their institution’s performance and make informed decisions to improve services.
- Patient Outcome Reports: Medical writers can use visual elements to create reports that summarize patient outcomes, such as treatment efficacy or recovery rates. These reports are useful for both clinicians and patients in assessing the success of a treatment plan.
By using graphical elements, medical writers can ensure that clinical reports are not only informative but also visually engaging, making it easier for healthcare professionals to absorb and act on the information.
How to Implement Data Visualization in the Healthcare Sector
Implementing data visualization in the healthcare sector requires careful planning and collaboration among various stakeholders. Medical writers can play a key role in this implementation by following these steps:
- Understand the Audience: Medical writers should tailor their visualizations based on the target audience, whether it’s clinicians, researchers, patients, or the public. Different audiences require different levels of complexity in their data presentations.
- Choose the Right Tools: There are numerous software tools available for creating data visualizations, including Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio. Medical writers should be familiar with these tools to create effective, professional-grade visualizations.
- Simplify Complex Data: The goal of visualization is to make data easier to understand. Medical writers should avoid overloading their visuals with too much information and focus on highlighting the most critical data points.
- Ensure Accuracy: Data visualization must accurately represent the underlying data. Medical writers need to collaborate with data analysts and healthcare professionals to ensure that the visualizations are both accurate and informative.
- Regularly Update Content: Healthcare data is constantly changing, and medical writers should ensure that their visual content is regularly updated to reflect the latest information and trends.
Read More: Navigating Predatory Publishing in Medical Communications: A Comprehensive Guide
AI and the Future of Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare, and data visualization is no exception. AI can process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and present insights in visual formats that are easy to interpret. For medical writers, this means that AI-driven tools can assist in creating more sophisticated and predictive visualizations.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze patient data to predict outcomes, such as the likelihood of disease progression or treatment success. Medical writers can incorporate these predictive models into their reports, helping clinicians make proactive decisions.
- Personalized Visualizations: AI can generate personalized visualizations based on individual patient data. For example, AI algorithms could create customized dashboards for patients to track their progress and understand their treatment plans.
- Streamlined Content Creation: AI-powered tools can help medical writers by automating parts of the content creation process, such as generating charts and graphs based on raw data inputs.
Conclusion
Data visualization is an indispensable tool in modern healthcare, offering a way to simplify complex data and communicate it effectively to a wide range of audiences. Medical writers, as key facilitators of healthcare communication, can harness the power of data visualization to enhance their content, making it more accessible, engaging, and impactful. As AI continues to shape the future of healthcare, the role of data visualization will only grow, creating exciting opportunities for medical writers to further improve how healthcare data is presented and understood.