The peer review process is a cornerstone of academic and scientific publishing. It serves as a quality control mechanism to ensure accuracy, reliability and contributes to the body of knowledge in each field. Despite its critical role, the peer review process can be sometimes complicated to understand. This blog aims to provide an in-depth look at the peer review process, exploring its various types, common challenges, and potential improvements to enhance transparency and efficiency.
What is Peer Review?
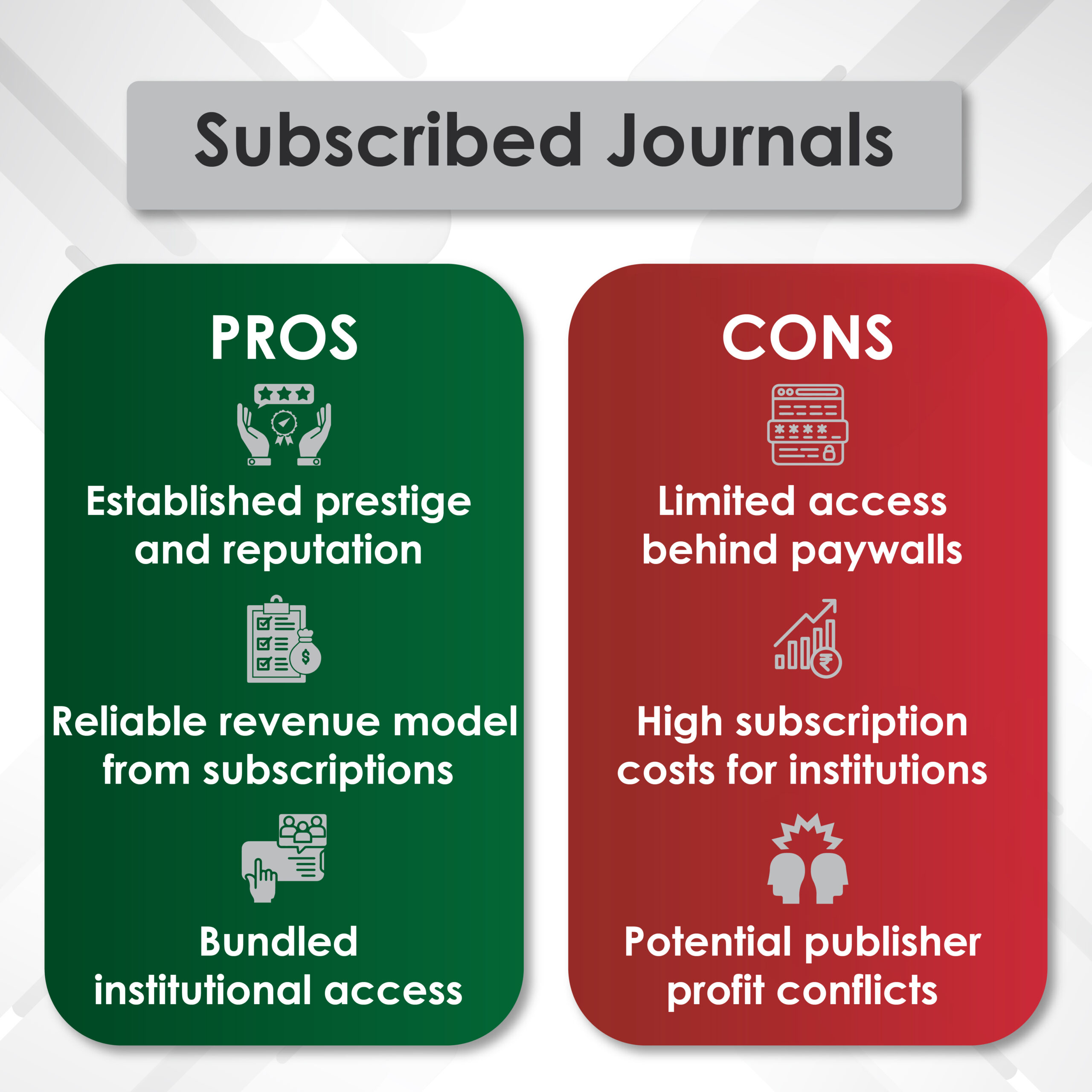
Peer review is a process in which work is evaluated by individuals who possess similar skill sets as the creators of the work, known as peers. It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. The main goals of peer review are to assess the validity, quality, and originality of research before publication.
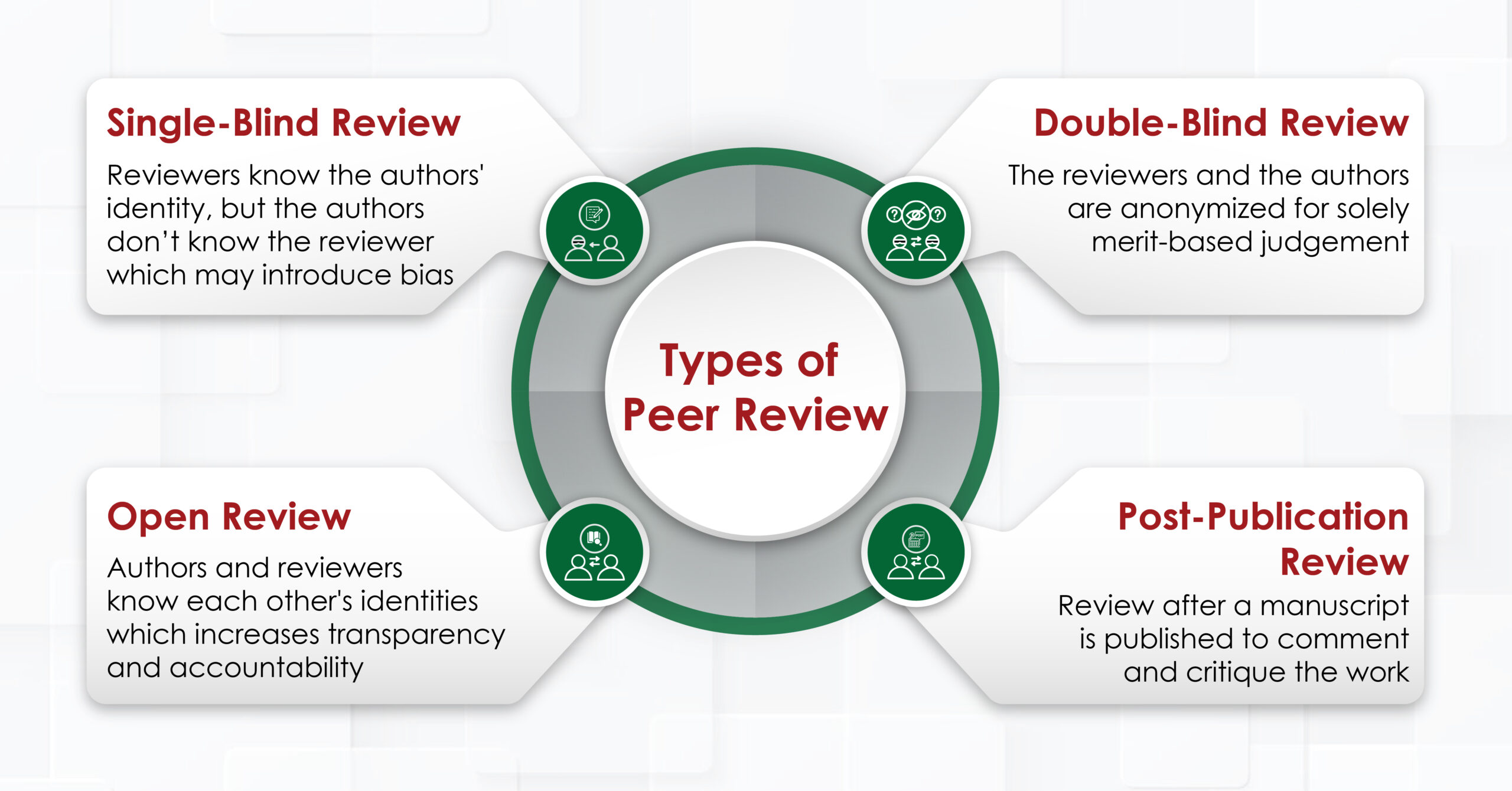
Types of Peer Review
a. Single-Blind Review
This review method involves reviewers knowing the authors’ identities, whereas the authors themselves are kept unaware of the reviewers. This type of peer review is the most used, as it allows reviewers to provide unbiased critiques without any personal relationships affecting their assessment. However, there is a potential for bias to arise if the reviewer is familiar with the author’s identity.
b. Double-Blind Review
In this type of review, both the reviewers and the authors are anonymized. This type of review is intended to eliminate any bias related to the author’s identity, such as their reputation, gender, or affiliation. The goal is to ensure that the manuscript is judged solely on its merits. However, achieving true anonymity can be challenging.
c. Open Review
This denotes a form of evaluation, where both the identities of the author and the reviewers are disclosed to each other. . This approach aims to increase transparency and accountability. Open review can take several forms, including publishing the reviewers’ names alongside their reviews or even making the reviews publicly available. While open review promotes accountability, it can also deter reviewers from providing honest critiques due to fear of conflict.
d. Post-Publication Review
These reviews occur after a manuscript has been published. This type of review, facilitated through online platforms, allows for valuable feedback and contributes to the enhancement of scholarly discourse. However, it can also lead to unmoderated or overly critical comments.
Common Challenges in Peer Review
a. Bias and Subjectivity
Despite efforts to minimize bias, it can still occur in peer review. Reviewers may be influenced by the authors’ identities, their own beliefs, or their relationships with the authors. Bias can affect the objectivity of the review and ultimately the quality of published research.
b. Lack of Transparency
The traditional peer review process is often criticized for its lack of transparency. Authors may not know why their work was rejected or what specific issues were identified by reviewers. This opacity can lead to frustration and a lack of trust in the process.
c. Reviewer Availability and Quality
Finding qualified reviewers who are willing to provide thorough and timely reviews is a significant challenge. Many reviewers are overburdened with their work and may not have the time to conduct detailed reviews. Additionally, the quality of reviews can vary significantly, with some reviewers providing only cursory feedback.
d. Time-Consuming Process
The peer review process can be time-consuming, often taking several months from submission to publication. This delay can be detrimental to researchers who need to publish their work quickly for career advancement or funding purposes.
e. Ethical Issues
These can arise in peer review, including plagiarism, conflicts of interest, and breaches of confidentiality. Reviewers must adhere to ethical guidelines to maintain the integrity of the process.
Improving Transparency and Efficiency in Peer Review
a. Adopting Open Review Practices
Increasing transparency in the peer review process can be achieved by adopting open review practices. Making reviewers’ identities and their reviews public can promote accountability and improve the quality of reviews. Additionally, publishing the decision letters and the authors’ responses can provide insights into the review process and the rationale behind editorial decisions.
b. Implementing Double-Blind Review
While challenging to implement perfectly, double-blind review can reduce bias and ensure that manuscripts are judged solely on their content. Journals can take steps to anonymize submissions and instruct authors on how to remove identifying information from their manuscripts.
c. Utilizing Technology
Advancements in technology can streamline the peer review process. Online submission systems, automated reviewer matching, and artificial intelligence tools can help manage the review workflow more efficiently. AI can assist in initial screenings, identifying potential reviewers, and detecting ethical issues such as plagiarism.
d. Providing Reviewer Training
Enhancing the quality of reviews can be achieved by providing training for reviewers. Many reviewers receive little to no formal training in how to conduct a peer review. Journals and academic institutions can offer workshops, guidelines, and mentorship programs to help reviewers develop their skills.
e. Recognizing Reviewers
Acknowledging and rewarding reviewers for their contributions can incentivize quality reviews and encourage more researchers to participate in the peer review process. Journals can provide certificates, offer discounts on publication fees, or recognize top reviewers publicly.
f. Expediting the Review Process
To reduce the time from submission to publication, journals can implement strategies to expedite the review process. These may include setting clear deadlines for reviewers, using fast-track options for high-priority research, and improving communication between editors, reviewers, and authors.
g. Encouraging Post-Publication Review
This can provide ongoing scrutiny and discussion of published research. Online platforms that facilitate post-publication comments and ratings can help identify any overlooked issues and keep the scientific discourse alive.
Conclusion
The peer review process is essential for maintaining the quality and credibility of scientific research. Despite its challenges, peer review remains a crucial component of academic publishing. Understanding the different types of peer review, recognizing common challenges, and exploring ways to improve transparency and efficiency, the academic community can enhance the effectiveness of this process. Continued efforts to refine and innovate peer review practices will ensure that it remains a potent mechanism for validating and disseminating scientific knowledge. Through transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement, the peer review process can better serve researchers, reviewers, and the wider scientific community.
We are Here!
Turacoz Healthcare Solutions, committed to enhancing scientific communication, is poised to enhance the peer review process by offering advanced manuscript management technology and promoting ethical review practices. Understanding the evolving landscape of academic publishing, Turacoz supports scholars with a comprehensive range of services, including book and thesis writing, authoring book chapters, and tailored academic support. Their expertise ensures that the peer review process remains robust, validating research and advancing knowledge. Partner with Turacoz for academic excellence and maximize your work’s potential in the digital age. Visit us at www.turacoz.com or share your queries at [email protected] and we will connect with you! .