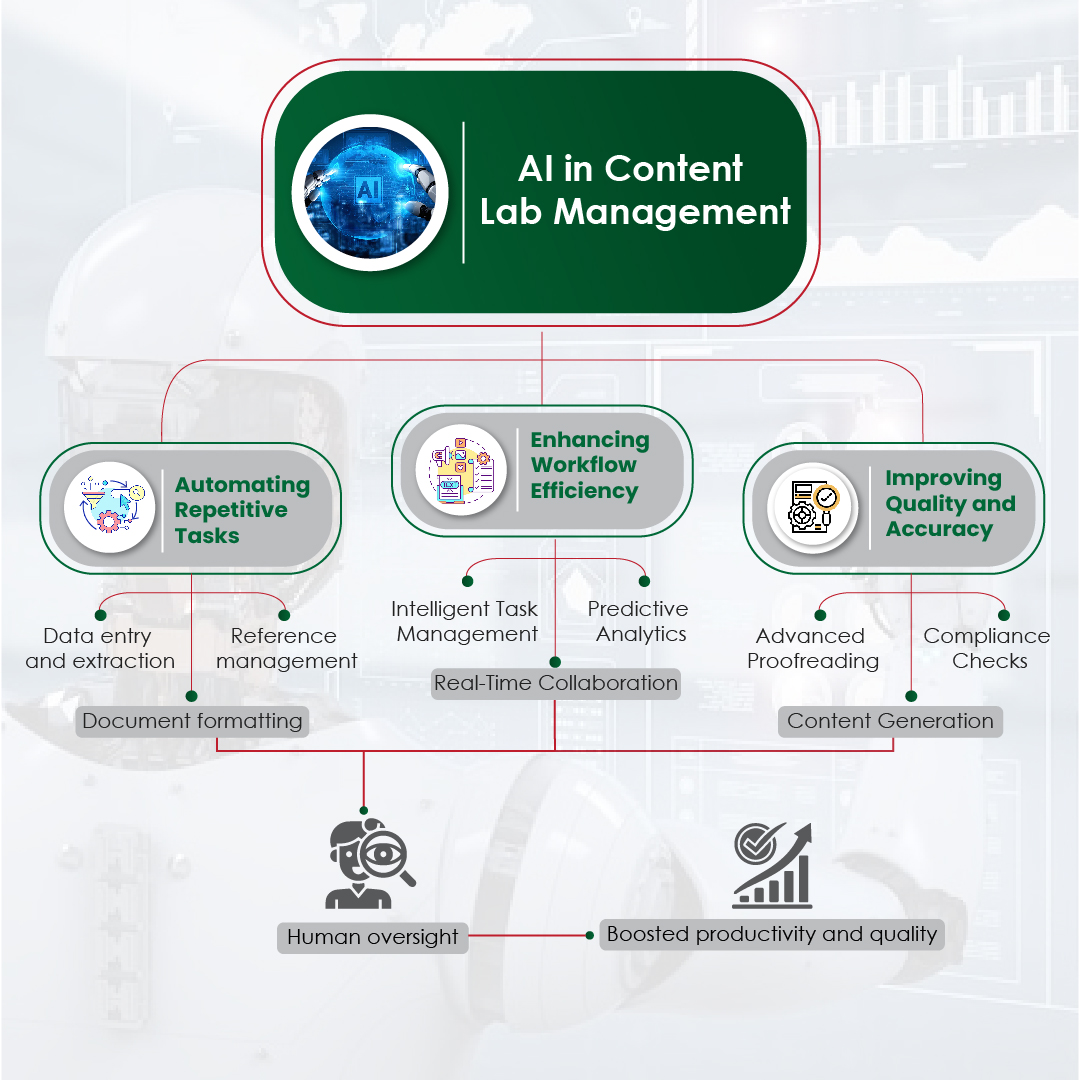
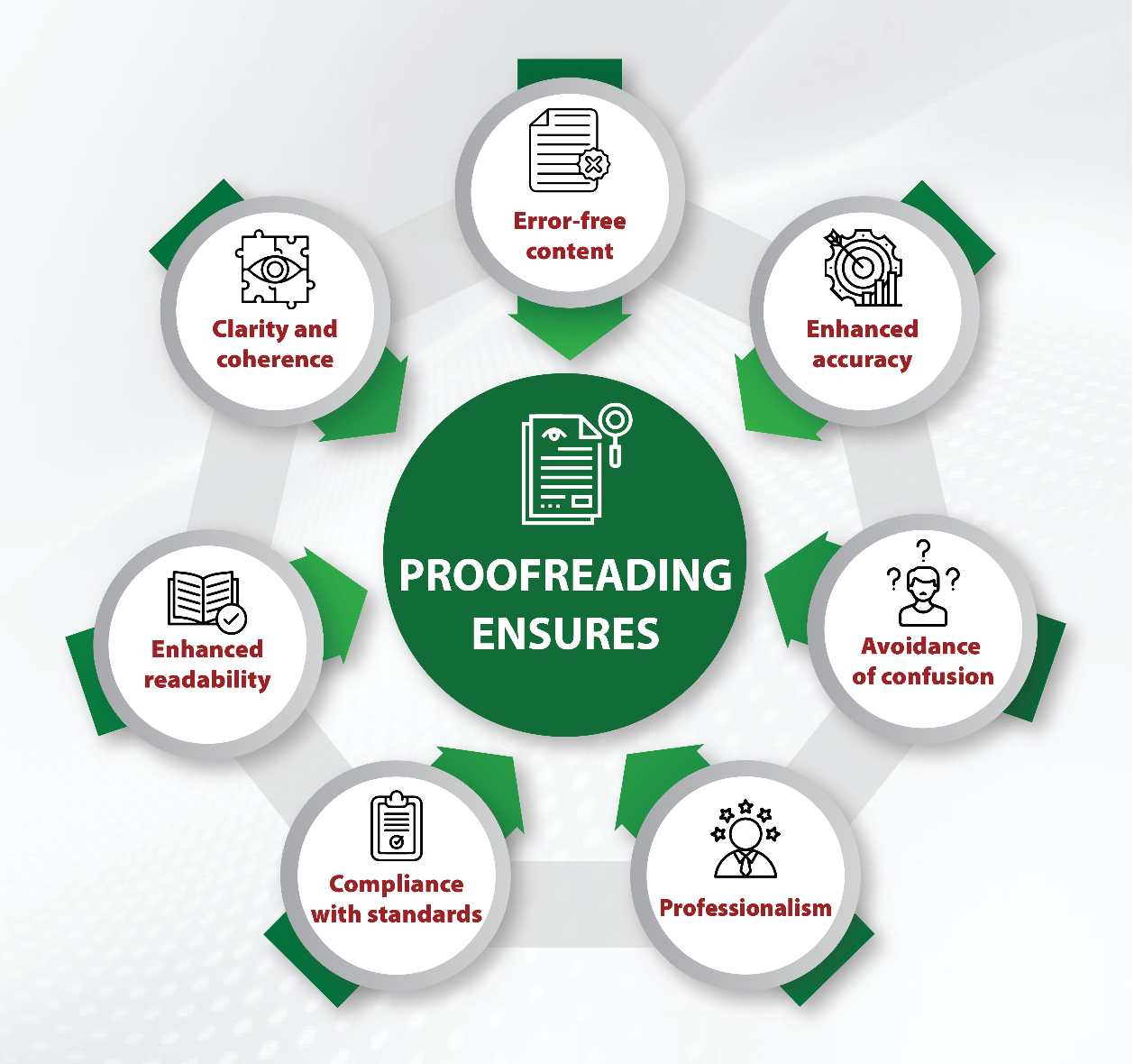
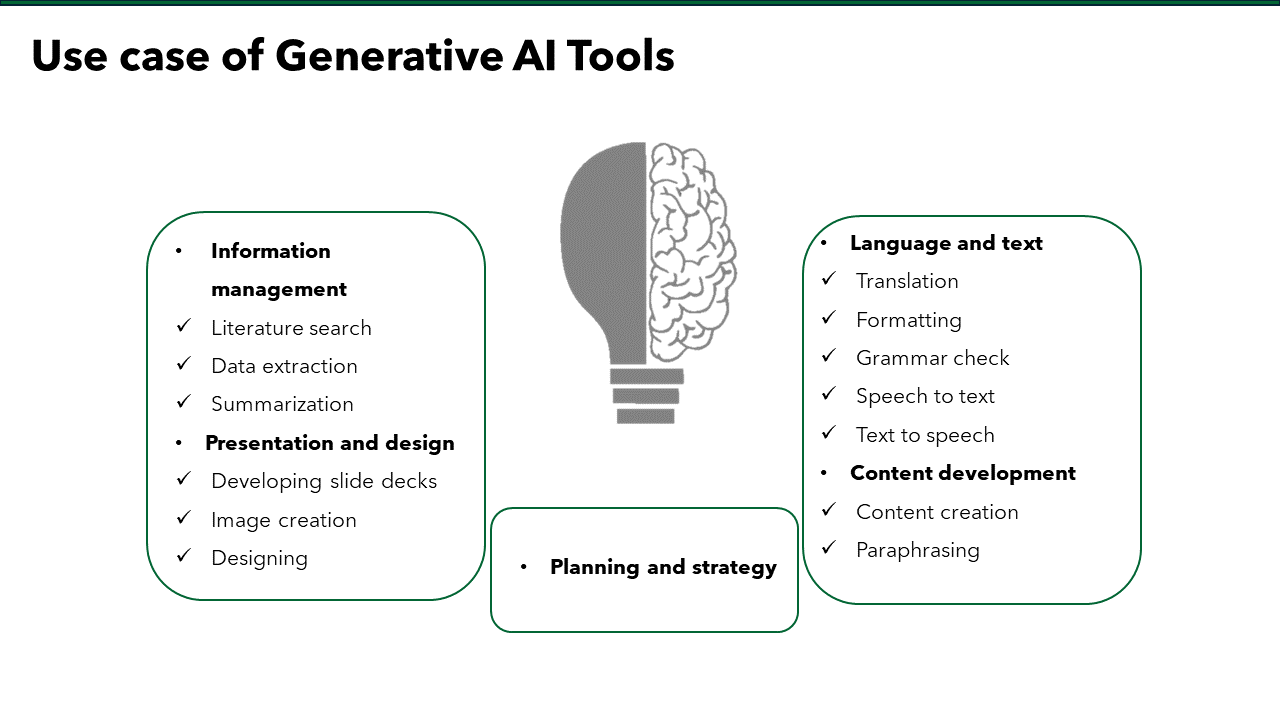
Are you finding it challenging to make your medical communications clear and engaging?
Navigating the world of medical content can sometimes feel like deciphering a foreign language, even for seasoned professionals. The goal of this blog is to help you create content that is clear, engaging, and most importantly, user-friendly. Let’s dive into some tips to help you communicate more effectively with your audience, whether they are healthcare professionals or patients.
- Know Your Audience
First and foremost, understanding your audience is crucial. Are you writing for healthcare professionals (HCPs) or patients?
The language and level of detail you use will differ greatly. For HCPs, you can use more technical terms and delve into complex details. For patients, however, it is essential to use plain language and avoid jargon. Always keep in mind who you are speaking to and tailor your message accordingly.
- Clarity is Key
Medical information can be complex, but your job is to make it as clear as possible. Use simple, straightforward language, and avoid long, convoluted sentences. Break down complex ideas into manageable chunks. Remember, the clearer your content, the easier it will be for your audience to understand and retain the information.
- Engage with Stories and Analogies
People love stories. They make information more relatable and memorable. Use real-life examples, patient stories, or analogies to explain complex medical concepts. For instance, describing the immune system as a “security system” that protects the body from intruders can make the concept more accessible to a layperson.
Read More: How to Write Medical Content That Ranks on Search Engines?
- Use Visual Aids
A picture is worth a thousand words, especially in medical communications. Diagrams, infographics, and videos can help illustrate your points and make your content more engaging. Visual aids are particularly helpful when explaining procedures, anatomy, or the effects of certain medications. Just make sure that your visuals are clear and accurately represent the information you are conveying.
- Make It Interactive
Interactive content can greatly enhance user engagement. Consider incorporating quizzes, interactive diagrams, or clickable links that provide additional information. Interactive elements can help reinforce learning and keep your audience engaged. For example, a quiz at the end of an article about diabetes management could help patients assess their understanding and encourage them to learn more.
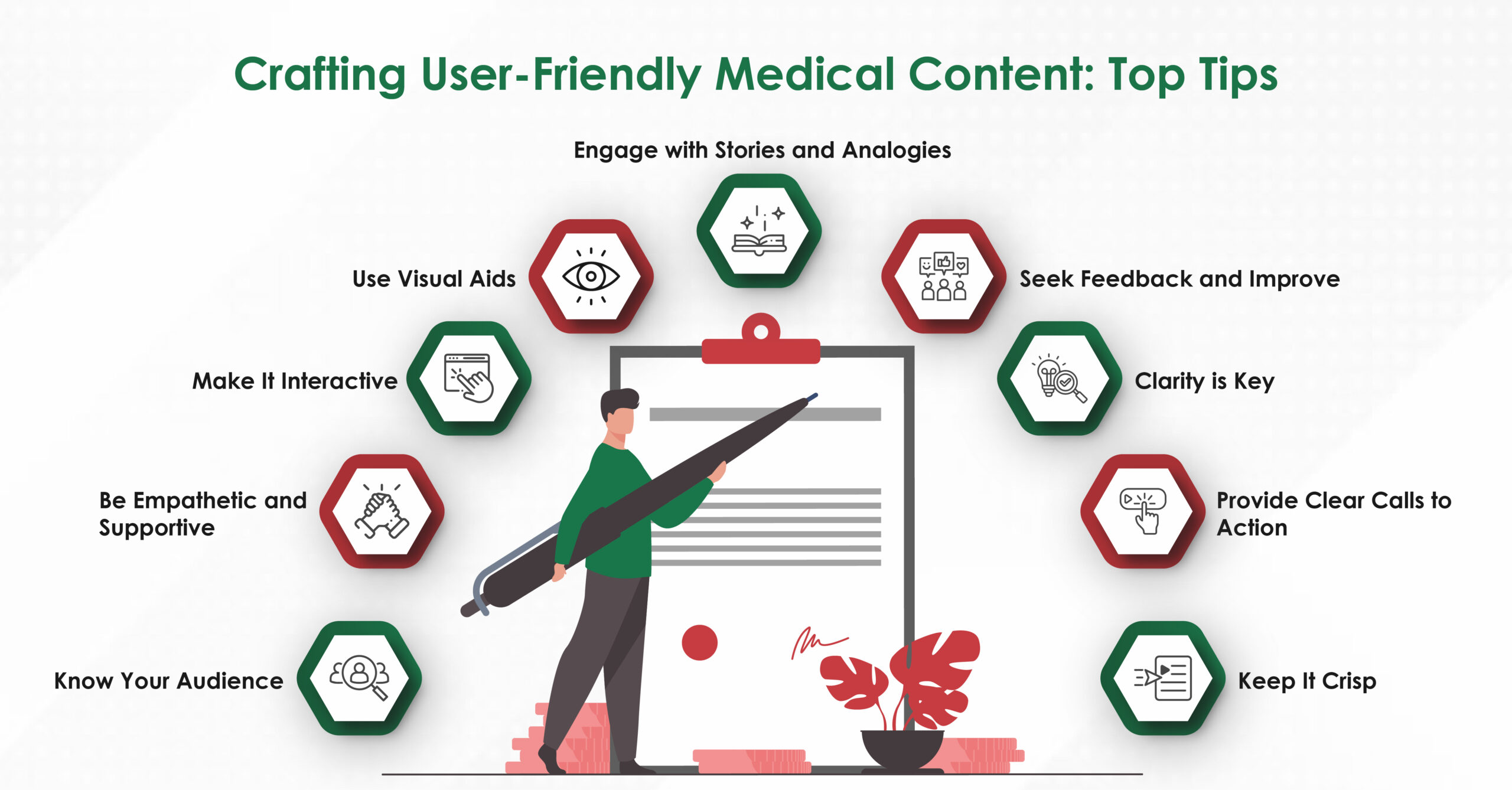
- Keep It Crisp
In today’s fast-paced world, attention spans are short. Keep your content concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary fluff, and focus on delivering valuable information. Bullet points, numbered lists, and short paragraphs can help break up the text and make it more digestible.
- Provide Clear Calls to Action
Whether you want your readers to schedule an appointment, read more about a condition, or follow a treatment plan, make sure your calls to action are clear and easy to follow. Use direct language and provide easy-to-follow instructions. For example, “Click here to book your appointment” is more effective than a vague “Learn more.”
- Be Empathetic and Supportive
Empathy goes a long way in medical communications. Acknowledge the emotional and physical challenges your audience may be facing, and offer support and encouragement. Use a friendly and reassuring tone. For example, instead of saying, “You must take your medication daily,” try, “Taking your medication daily can help you feel better and stay healthy. We’re here to support you every step of the way.”
- Seek Feedback and Improve
Finally, don’t be afraid to ask for feedback. Whether through surveys, comment sections, or direct conversations, gather insights from your audience about what works and what doesn’t. Use this feedback to continuously improve your content and better meet the needs of your readers.
In conclusion, making your medical content user-friendly is all about clarity, engagement, and empathy. By knowing your audience, using simple language, incorporating visuals, and being supportive, you can create content that truly resonates with your readers.
Happy writing!
For more information or assistance, feel free to reach out to us at [email protected].