Publishing research is a significant achievement in an academic or scientific journey. It not only adds to the global knowledge pool but also enhances the reputation and credibility of researchers. However, the path to publication can be complex and time-consuming, especially with the stringent standards and intense competition in the academic publishing realm. In such a landscape, scientific publishing services play a crucial role as trusted guides, leading researchers through the intricate process of manuscript preparation, submission, and publication. Let’s explore how these services can simplify the journey from research to publication.
About Scientific Publishing Services
Scientific publishing services are instrumental in facilitating research publication by offering expert assistance to authors, healthcare professionals, and students. These comprehensive services are designed to help authors navigate the complex and often confusing process of manuscript preparation, submission, and publication. The advantages of using scientific publishing services are numerous and can significantly enhance the chances of publishing research in a reputable journal. It assures the authors that their work is in capable hands, ensuring their research is published smoothly and without any complications.

Benefits of Scientific Publishing Services
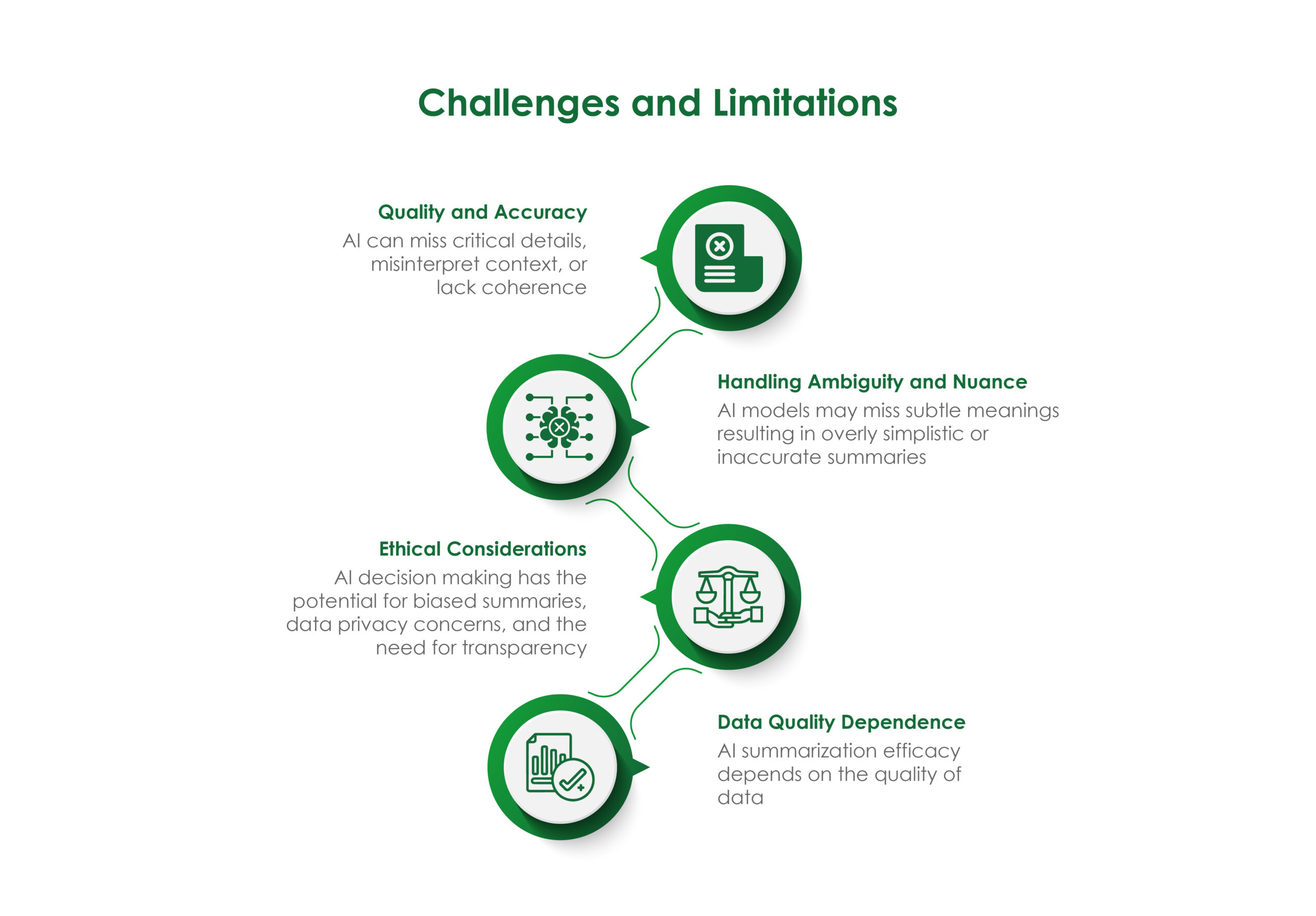
- Quality Editing and Proofreading: Scientific publishing services provide thorough editing and proofreading of your manuscript. This ensures that your research is free of errors and written concisely and effectively, increasing the chances of your research being accepted for publication.
- Formatting: Different journals have different formatting requirements. Scientific publishing services are familiar with these requirements and can format your manuscript accordingly. This saves you time and ensures that your manuscript meets the standards of the target journal.
- Targeted Journal Selection: Scientific publishing services can help you select the most appropriate journal for your research, increasing the chances of your research being accepted for publication.
- Improved Chances of Publication: Scientific publishing services can help you navigate the submission process and increase your chances of publication. They know what journals are looking for and can help you tailor your research to meet their requirements. This may involve making your research more accessible to a broader audience, ensuring it aligns with the journal’s scope and aims, and addressing any specific formatting or language requirements. Doing so increases the likelihood of your research being accepted for publication.
- Time-saving: Scientific publishing services can save you time. They can handle the time-consuming formatting, editing, and proofreading tasks, allowing you to focus on your research. This efficiency boost can make you feel more productive and less overwhelmed by the publishing process.
Enhancing Scholarly Impact
- Leveraging Specialized Expertise
Scientific publishing services offer access to specialized professionals who provide tailored guidance and support that aligns with the intricacies of authors’ research. These specialized editors and consultants enhance the scholarly rigor and credibility of the manuscript by helping authors navigate technical terminology, ensure accuracy, and address discipline-specific conventions. By leveraging specialized expertise, authors can improve the quality and impact of their research, increasing its potential for publication success.
- Maximizing the Visibility and Impact of Research
Scientific publishing services use various tactics like crafting compelling abstracts and keywords, optimizing search engine visibility, and social media outreach to enhance the discoverability and accessibility of research. They also help engage with the target audience through targeted promotion and networking activities. By maximizing visibility and impact, authors can extend the reach and influence of their research, amplifying its contribution to knowledge advancement and fostering meaningful dialogue. Scientific publishing services empower authors to make a lasting impact, leaving a lasting imprint on their respective fields.
- Embracing Open-access Initiatives
Open-access initiatives promote transparency, accessibility, and inclusivity in scholarly publishing. Scientific publishing services help authors navigate open-access publishing options by selecting reputable journals and repositories and guiding them through the intricacies of open-access publishing. By embracing open-access initiatives, authors can maximize the impact of their research, make knowledge accessible to a global audience, and contribute to advancing science and scholarship.
- Nurturing Ethical Scholarship
Scientific publishing services prioritize integrity and ethical conduct by adhering to strict editorial standards, ethical guidelines, and best practices in academic publishing. These services uphold accountability and integrity at every stage of the publication process and help authors navigate ethical dilemmas. By fostering ethical scholarship, these services maintain the credibility and trustworthiness of the scholarly literature, safeguard the integrity of the research enterprise, and promote public confidence in science and academia.
How to Choose the Right Scientific Publishing Service?
Choosing an exemplary scientific publishing service is essential. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a scientific publishing service:
- Reputation: Look for a scientific publishing service with a good reputation. Check reviews and testimonials from previous clients.
- Experience: Look for a scientific publishing service with experience in your field. This ensures that they are familiar with the standards and requirements of the target journal.
- Quality of Service: Look for a scientific publishing service that provides quality service. This includes thorough editing and proofreading, timely delivery, and excellent customer service.
- Cost: Look for a scientific publishing service that offers competitive pricing. Competitive pricing means the service’s rates align with industry standards and reflect the quality and range of services provided. Compare prices and services before deciding to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money.
Getting your research published can be a challenging task. However, scientific publishing services can help you navigate the process and increase your chances of getting published. They provide quality editing and proofreading, formatting, targeted journal selection, improved chances of publication, and save you time. However, it’s important to note that scientific publishing services may not guarantee publication, and the final decision rests with the journal’s editorial board. When choosing a scientific publishing service, consider their reputation, experience, quality of service, and cost. With the exemplary scientific publishing service, you can get your research published and contribute to the growth of knowledge in your field.
At Turacoz, we pride ourselves on offering exemplary scientific publication services to healthcare professionals, medical writers, students, researchers, pharma companies, and other healthcare organizations. Our expert team members are dedicated to providing top-notch editing, formatting, and journal selection assistance at competitive prices. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher looking to streamline the publication process or a student seeking guidance on manuscript preparation, we have the expertise and resources to meet your needs. You can contact us at [email protected] with your queries.