Artificial Intelligence (AI) has already begun to revolutionize numerous industries, and medical affairs is no exception. As the technology continues to evolve, it promises to bring profound changes to how medical professionals manage and disseminate information, interact with stakeholders, and maintain compliance. This blog explores the multifaceted impact of AI on medical affairs, focusing on key areas such as generative AI and prompt engineering, managing organizational behavior, augmenting content generation, and creatively presenting scientific information.
Generative AI and Prompt Engineering
A subset of artificial intelligence that involves creating new content based on existing data, holds immense potential for medical affairs. Prompt engineering, the process of designing prompts to guide AI in generating relevant and accurate content, is a critical aspect of leveraging this technology effectively.
- Enhanced Data Analysis and Insights: Generative AI can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including clinical trial results, patient records, and scientific literature, to generate meaningful insights. These insights can help medical affairs professionals make informed decisions, identify trends, and anticipate future developments in the medical field. For example, AI can identify potential side effects of new drugs by analyzing patient data from clinical trials, thereby enhancing patient safety and accelerating the approval process.
- Personalized Medical Communication: Prompt engineering enables AI to generate personalized communication tailored to the needs of different stakeholders, such as healthcare professionals, patients, and regulatory bodies. By crafting precise prompts, medical affairs teams can ensure that the AI produces accurate, relevant, and comprehensible information. This personalized approach can improve stakeholder engagement and facilitate better understanding of complex medical information.
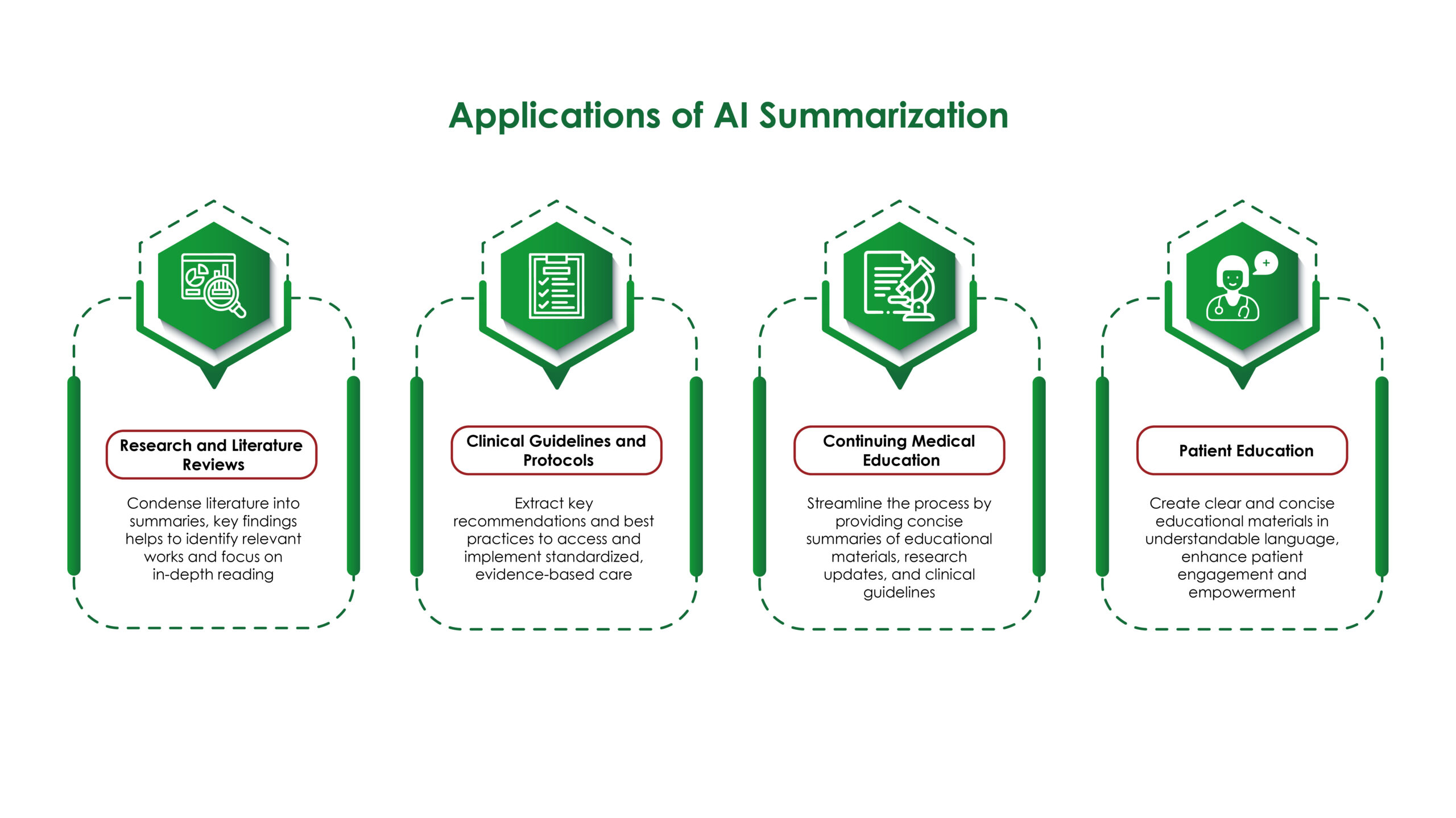
- Efficient Literature Reviews: Conducting literature reviews is a time-consuming but essential task in medical affairs. Generative AI can automate this process by quickly summarizing vast amounts of scientific literature and highlighting key findings. This allows medical professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest research without spending countless hours sifting through papers.
Managing Organizational Behavior
The integration of AI into medical affairs requires careful management of organizational behavior to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of the technology.
- Change Management: Introducing AI tools necessitates a shift in organizational culture. Employees may resist adopting new technologies due to fear of job displacement or a lack of understanding of how these tools work. Effective change management strategies, including training programs, transparent communication, and involving employees in the implementation process, can help overcome these challenges.
- Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Teams: AI in medical affairs often requires collaboration between various departments, including IT, data science, and medical teams. Fostering interdisciplinary collaboration ensures that AI tools are effectively integrated and utilized. By bringing together diverse expertise, organizations can develop more robust AI solutions and address potential issues from multiple perspectives.
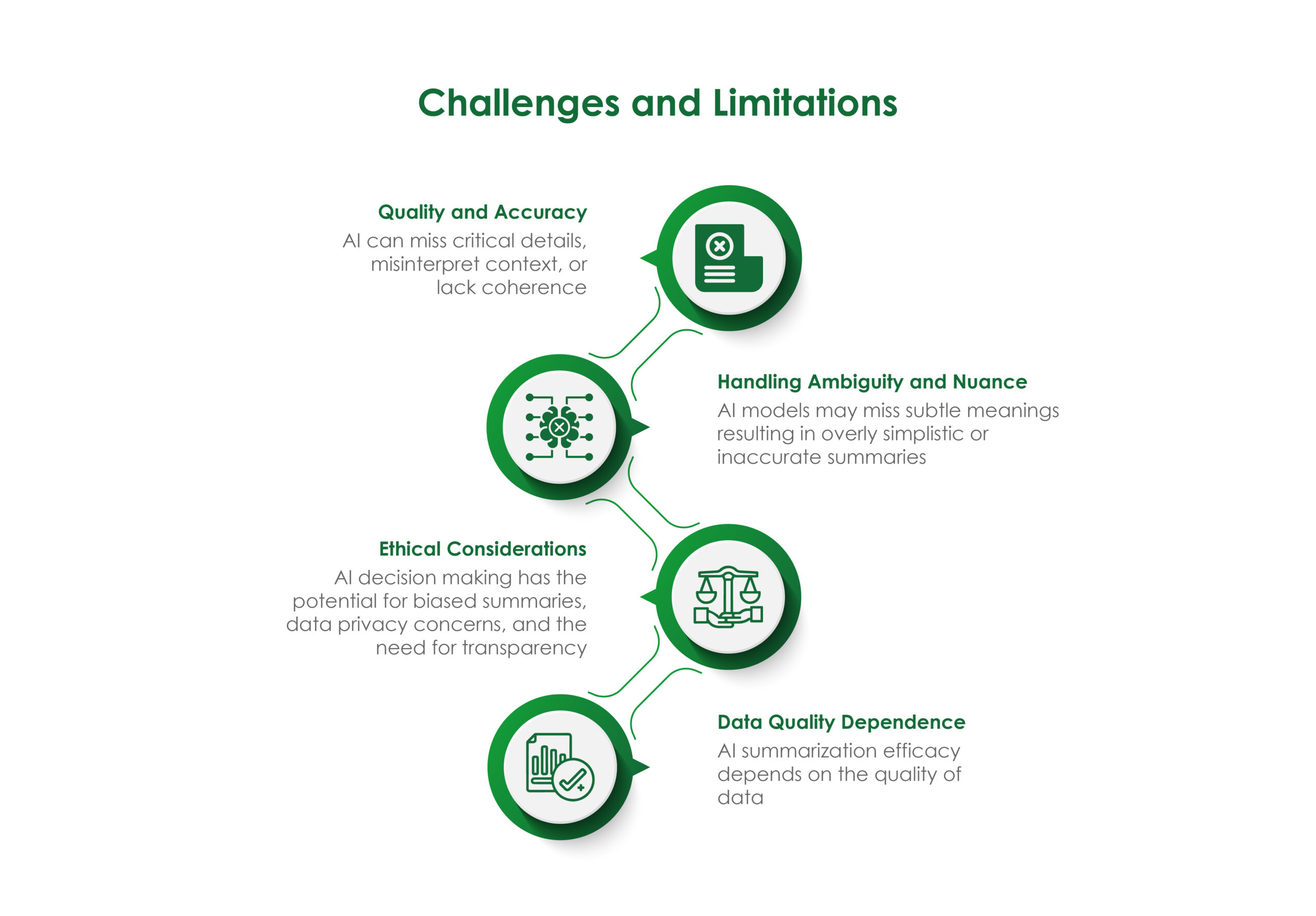
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI in medical affairs raises ethical questions, such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse. Organizations must establish ethical guidelines and ensure compliance with regulations to address these concerns. Transparent policies and regular audits can help build trust among stakeholders and maintain the integrity of medical affairs operations.
Augmentation of Content Generation by Generative AI Tools
Generative AI tools can significantly enhance content generation in medical affairs, enabling the creation of high-quality, accurate, and engaging materials.
- Automated Report Generation: AI can automate the generation of various reports, such as clinical trial reports, regulatory submissions, and medical publications. By analyzing data and generating structured reports, AI reduces the time and effort required for these tasks, allowing medical professionals to focus on more strategic activities.
- Consistency and Accuracy: AI ensures consistency and accuracy in content generation by minimizing human errors and standardizing information. This is particularly important in medical affairs, where precise and reliable information is crucial. AI-generated content can be cross-verified with existing data to ensure its accuracy before dissemination.
- Multilingual Content: In a globalized world, medical affairs professionals often need to communicate in multiple languages. Generative AI tools can translate and adapt content for different linguistic and cultural contexts, ensuring that information is accessible to a broader audience. This capability enhances global collaboration and improves the dissemination of medical knowledge.
Generative AI Tools and Creative Presentation of Science
AI tools are not only proficient at generating content but also excel in presenting scientific information in innovative and engaging ways.
- Interactive Visualizations: AI can create interactive visualizations that help explain complex scientific concepts and data. For instance, AI-generated graphs, charts, and 3D models can make it easier for stakeholders to understand clinical trial results or the mechanism of action of a new drug. These visualizations can be tailored to different audiences, from healthcare professionals to patients.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Generative AI can power VR and AR applications that provide immersive experiences for medical education and training. For example, medical professionals can use VR to explore detailed 3D models of the human body or simulate surgical procedures. AR can enhance presentations by overlaying digital information onto the physical world, making scientific explanations more interactive and engaging.
- Customizable Content: AI enables the customization of scientific content based on the preferences and needs of the audience. For instance, AI can generate different versions of a presentation for a technical audience and a lay audience, ensuring that the information is appropriately detailed and understandable for each group. This customization enhances the effectiveness of communication and increases audience engagement.
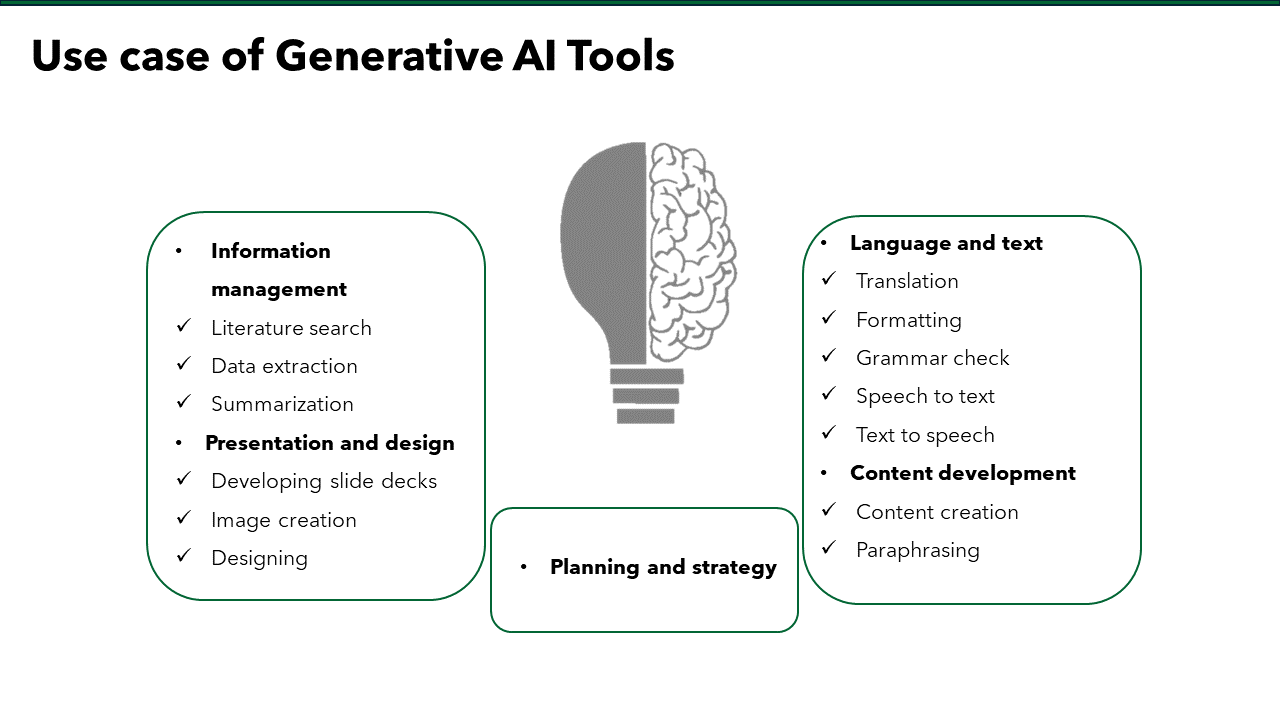
Artificial Intelligence is poised to transform medical affairs in profound ways. Generative AI and prompt engineering are enhancing data analysis, personalizing communication, and streamlining literature reviews. Managing organizational behavior is crucial for successful AI integration, requiring effective change management, interdisciplinary collaboration, and adherence to ethical standards. Generative AI tools are augmenting content generation by automating reports, ensuring consistency, and translating content for a global audience. Moreover, AI is revolutionizing the presentation of scientific information through interactive visualizations, VR and AR applications, and customizable content.
The future of medical affairs with AI is bright, with continuous learning, integration with other technologies, and the democratization of medical knowledge paving the way for more efficient and effective healthcare. Embracing AI in medical affairs not only enhances the capabilities of medical professionals but also ultimately improves patient outcomes and advances the field of medicine.