Scientific publishing is a cornerstone of academic and research progress that involves presenting the latest discoveries, fostering collaboration, and driving innovation across diverse fields. However, traditional publishing processes are often slow, costly, and inefficient, raising the need for streamlining scientific publishing services to enhance the efficiency and impact of research. In today’s fast-paced digital world, optimized publication services are crucial for maintaining competitiveness and relevance, which can be achieved by improving workflows and utilizing automation tools. Optimizing these services can create an efficient platform for researchers to share groundbreaking discoveries effectively. These improved publishing services address challenges in the scientific publication process and enable a rapid peer review process, leading to effective dissemination of research findings.
The Current Landscape
The conventional scientific publishing process involves the following steps:
- Manuscript Submission: Researchers submit their manuscripts to journals for evaluation as a part of communicating their research findings to the global community.
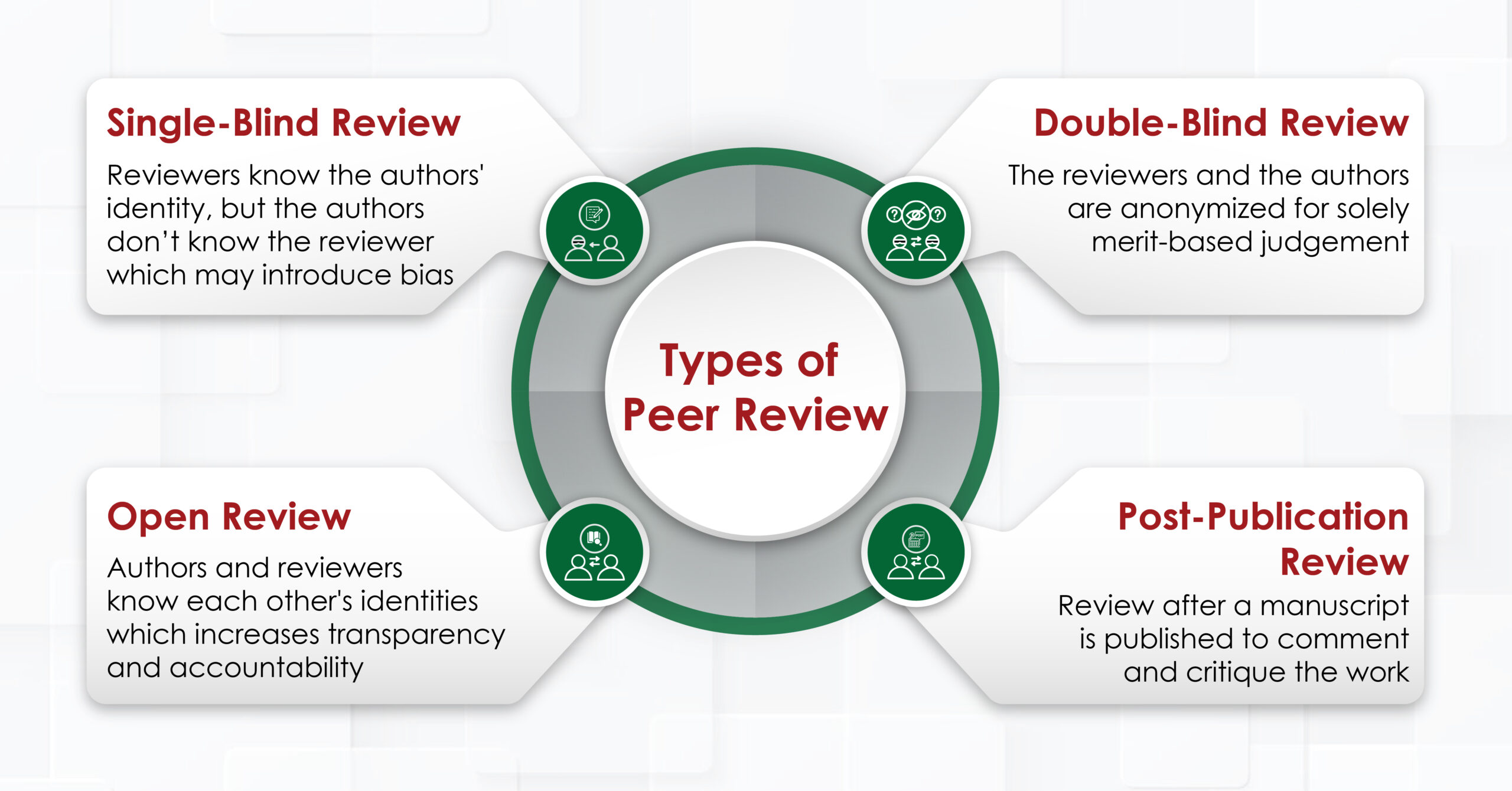
- Peer Review: This is an expert review of the submitted manuscript done by professionals in the respective domains to evaluate the validity, significance, and originality.
- Editing and Formatting: The accepted manuscripts are subjected to editing and formatting to meet publication standards.
- Publication: Once the manuscript has successfully undergone peer review, editing, and formatting, the final version is published and made accessible to the scientific community.
Challenges Associated with the Current Publishing Processes
- Lengthy Review Cycles: The traditional peer review process often involves multiple rounds of revisions and can take several months, delaying the dissemination of research results.
- Fragmented Dissemination of Research: With the availability of numerous journals and publication platforms, it can be difficult for researchers to reach their target audience effectively and for readers to find relevant and reliable scientific information.
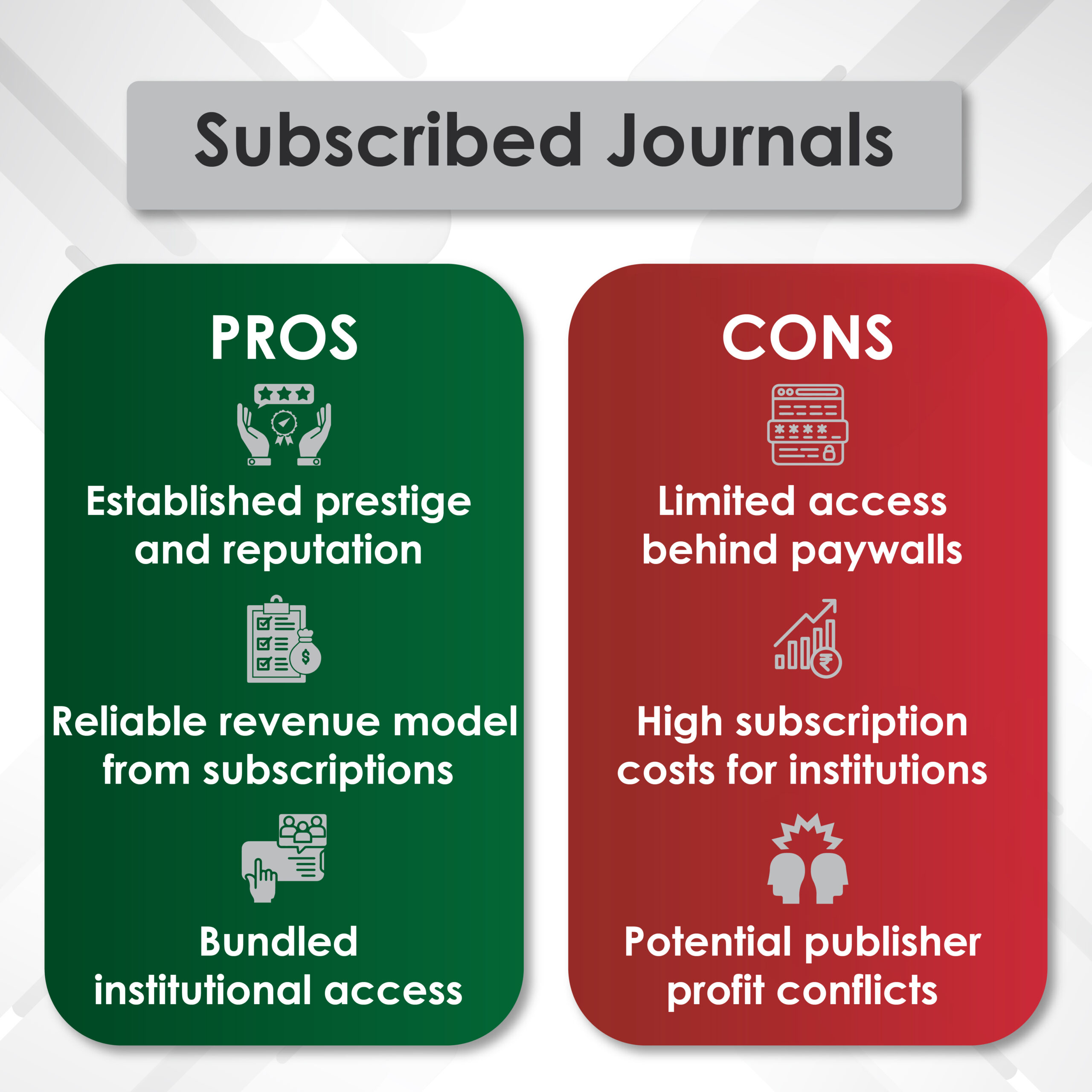
- Access and Accessibility Issues: High costs associated with publishing in reputable journals and the limited accessibility to scientific articles pose barriers for researchers and readers, particularly in developing countries.
The Need for Streamlining
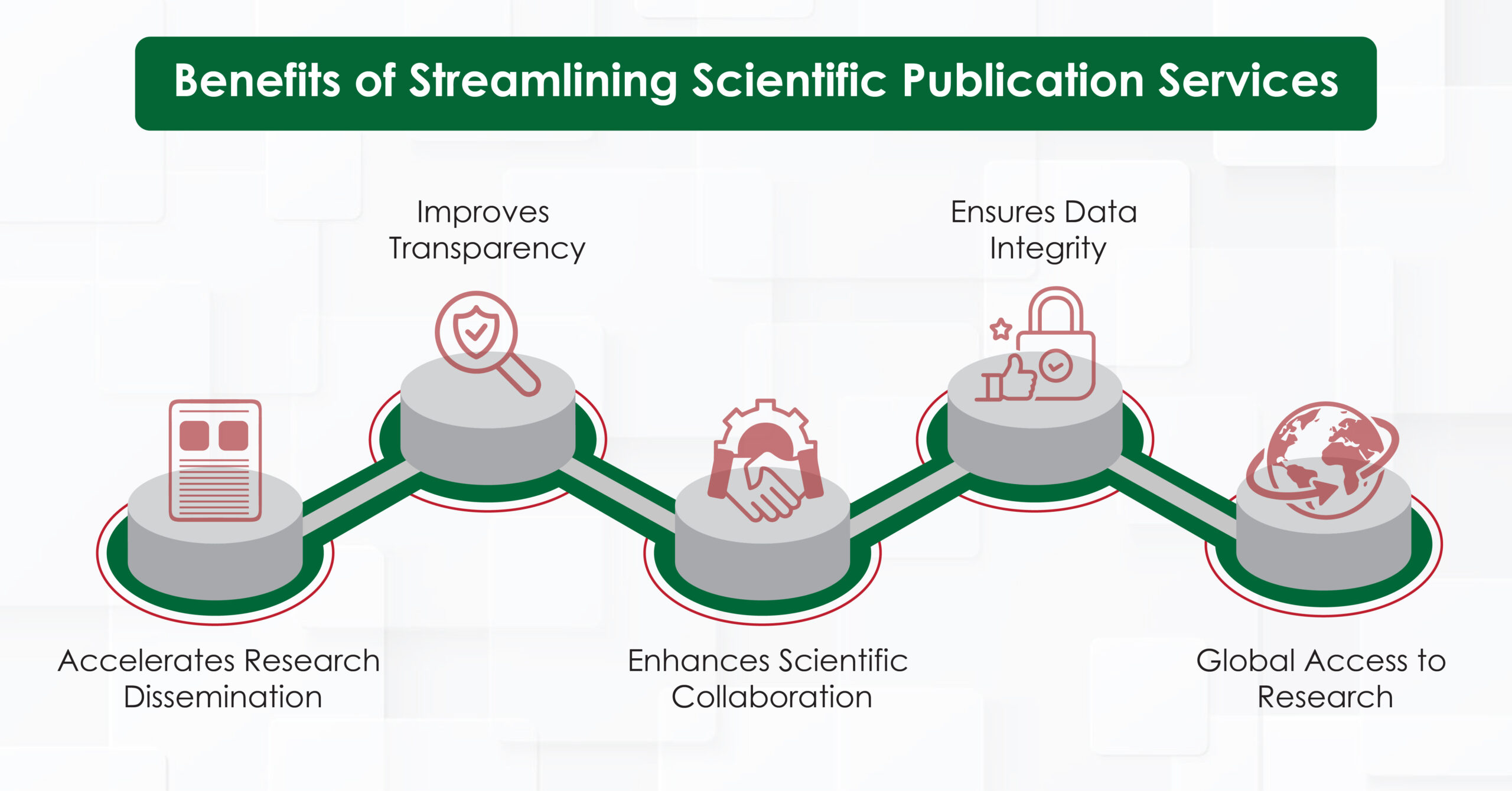
Streamlining scientific publishing can address these challenges and offer numerous benefits:
- Accelerated Dissemination of Research Findings: Research publication can be sped up by expedited review and publication processes which result in quick communication of novel insights, reducing time for peer review, editing, and formatting.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Research: Efficient publishing mechanisms provide an interdisciplinary collaboration by improving the accessibility of research.
- Global Accessibility Through Open-Access Initiatives: Open-access models ensure that research findings are universally accessible, regardless of financial constraints, promoting widespread dissemination of knowledge.
- Ensuring Data Integrity and Transparency: Improved processes can enhance the reliability and transparency of published research, promoting trust and credibility among the scientific community.
Innovations in Streamlining Services
Various strategies help streamline scientific publishing services to enhance efficiency and create an impact across researchers, readers, and the scientific community.
- AI and Machine Learning for Manuscript Screening and Peer Review: Implementing digital tools and AI for automated tasks like plagiarism checks and manuscript formatting to accelerate the process can streamline publication. These advanced technologies can enhance the initial review process by swiftly identifying potential issues and providing insights for a more efficient process.
- Blockchain for Authentication and Data Integrity: Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent solution for tracking the publication process, ensuring data integrity, and safeguarding the credibility of research findings throughout the entire publishing lifecycle.
- Open-Access and Open Peer Review Models: Opting for open-access platforms to enable public access to research can amplify its reach and impact. Open peer review promotes transparency, accountability, and constructive feedback among researchers by disclosing reviewer identities and making review comments publicly available.
- Collaborative Tools for Streamlined Workflows: Employing various efficient collaborative tools to benefit researchers, readers, and the broader scientific community promotes and simplifies submission and review processes making it crucial in enhancing scientific publishing efficiency.
- Integrated Research Dissemination: Utilizing the power of social networking sites by leveraging social media and digital platforms can broaden research outreach, enhance engagement with a diverse audience, and maximize dissemination impact effectively.
Future Directions
Enhancing the efficiency and impact of scientific publishing can be achieved through several key strategies and considerations:
- Community Engagement and Best Practices: It is essential to actively promote collaboration and exchange of best practices within the scientific community for ongoing enhancement. Promoting transparent communication and teamwork among scientists can result in more creative solutions and superior research results. Workshops, conferences, and online forums can play a role in enabling the sharing of ideas and experiences, contributing to the establishment and dissemination of best practices in scientific publishing.
- Policy and Funding Support for Open Access: Governments and funding organizations have a crucial role in advancing open-access initiatives. By providing financial backing and establishing policies that endorse open-access publication, these bodies can ensure that research discoveries are readily available to the global scientific community and the public. Open access models can eliminate financial barriers, enabling worldwide researchers, including those in developing nations, to reach and participate in the scientific conversation. This widespread accessibility has the potential to hasten the pace of discovery and innovation.
- Upholding Ethical Standards in Publishing: Ensuring that scientific research maintains high ethical standards is crucial to protect the integrity and credibility of the work. It involves verifying the accuracy and dependability of published data, avoiding conflicts of interest, and preventing plagiarism and other forms of academic misconduct. Journals and publishers should establish and enforce strict ethical guidelines and review processes to guarantee that all published research complies with these standards. By adhering to these principles, the scientific community can foster trust with the public and ensure that scientific progress involves robust and ethical research practices.
Conclusion
Streamlining scientific publishing is essential for enhancing the efficiency and impact of research communication. Embracing technological innovations, improving workflows, and promoting open access, can help the scientific community overcome current challenges and create a more effective research ecosystem. Stakeholders in the scientific community must collaborate and innovate advanced strategies for streamlining scientific publishing to achieve these improvements. This process will ensure swift and extensive communication of scientific knowledge, driving progress across all disciplines.
Ready to revolutionize your scientific publishing experience?
Chat with our experts today. At Turacoz, we are committed to making scientific research publications effective, and tailor our services to meet the industry’s needs. Partner with Turacoz for academic excellence and maximize your work’s outreach. Visit us at www.turacoz.com or share your queries at [email protected] and we will connect with you!